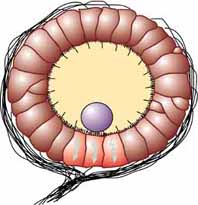
Statocyst
Statocyst is a sensory organ found in many aquatic invertebrates, including crustaceans, cephalopods, and some species of mollusks and annelids. It serves as a balance and orientation organ, helping these animals to sense their position relative to gravity. This is crucial for maintaining equilibrium, navigating through their environment, and for spatial orientation.
Structure[edit | edit source]
The statocyst is typically a small, fluid-filled sac or cavity. Inside the cavity, there are one or more dense, calcareous particles known as statoliths. The walls of the statocyst are lined with sensory hairs (cilia). When an animal moves or changes its orientation, the statoliths press against the sensory hairs, sending signals to the nervous system about the animal's position relative to gravity.
Function[edit | edit source]
The primary function of the statocyst is to provide the animal with a sense of equilibrium and spatial orientation. By detecting changes in position and movement, the statocyst helps the animal to correct its posture, maintain balance, and navigate through its environment. This is particularly important for aquatic animals, where buoyancy can affect their orientation and movement.
Evolution and Diversity[edit | edit source]
The statocyst represents an evolutionary solution to the challenge of spatial orientation in a three-dimensional environment. While the basic principle of operation is similar across different species, there is considerable variation in the complexity and structure of statocysts among different groups of invertebrates. This diversity reflects the adaptation of the statocyst to the specific ecological niches and lifestyles of different organisms.
Comparative Biology[edit | edit source]
In comparison to the vestibular system of vertebrates, which includes structures such as the semicircular canals and otolith organs, the statocyst offers a simpler mechanism for balance and orientation. However, both systems serve the same fundamental purpose of helping organisms maintain their equilibrium and navigate through their environment.
Research and Implications[edit | edit source]
Research into the function and structure of statocysts can provide insights into the evolutionary biology of sensory systems. Understanding how statocysts work can also have practical implications, including the development of new technologies for navigation and balance in robotics and artificial intelligence.
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD