Supercritical fluid
Supercritical fluid is a state of matter that occurs when a substance is subjected to temperature and pressure above its critical point. At this point, the distinctions between liquid and gas phases disappear, resulting in unique properties that are different from traditional liquids or gases. Supercritical fluids can diffuse through solids like a gas and dissolve materials like a liquid. This combination of properties makes supercritical fluids extremely useful in various industrial and scientific applications, including extraction, chemical reactions, and as solvents in chromatography.
Properties[edit | edit source]
Supercritical fluids exhibit properties that are intermediate between gases and liquids. They have the ability to dissolve materials like liquids but can also penetrate through materials like gases. The density of a supercritical fluid is similar to that of a liquid, while its viscosity is closer to that of a gas. Additionally, the diffusivity of supercritical fluids is higher than that of liquids, which facilitates faster mass transfer rates.
Critical Point[edit | edit source]
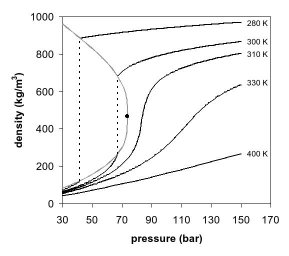
The critical point of a substance is the highest temperature and pressure at which the substance can exist as a liquid and gas in equilibrium. Beyond this point, the liquid and gas phases merge into a single supercritical phase. The critical temperature and pressure vary from one substance to another. For example, the critical point of carbon dioxide (CO2) is at a temperature of 31.10°C and a pressure of 73.8 bar, which makes CO2 one of the most commonly used supercritical fluids due to its moderate critical point.
Applications[edit | edit source]
Supercritical fluids have a wide range of applications across various industries:
Extraction[edit | edit source]
Supercritical fluid extraction (SFE) is a process that uses supercritical fluids as solvents to separate one component from another. It is widely used in the food, pharmaceutical, and environmental sectors. For instance, supercritical CO2 is used to decaffeinate coffee and tea, extract flavors and fragrances, and for the extraction of essential oils.
Chromatography[edit | edit source]
Supercritical fluid chromatography (SFC) is an analytical technique that utilizes supercritical fluids as the mobile phase. It combines the high efficiency of liquid chromatography with the high speed of gas chromatography. SFC is particularly useful for the separation of chiral compounds and is widely used in the pharmaceutical industry.
Chemical Reactions[edit | edit source]
Supercritical fluids can also act as reaction media for chemical reactions. The unique properties of supercritical fluids, such as enhanced mass transfer and tunable solvency, can lead to higher reaction rates and selectivities. Supercritical water oxidation (SCWO) is a process that uses supercritical water to oxidize hazardous wastes, offering an environmentally friendly alternative to traditional waste treatment methods.
Environmental Impact[edit | edit source]
The use of supercritical fluids, particularly CO2, is considered environmentally benign in many applications. Supercritical CO2 is non-toxic, non-flammable, and can be derived from industrial byproducts, making it an attractive solvent for green chemistry applications. Furthermore, the process conditions for supercritical fluid extraction and chromatography often eliminate the need for harmful organic solvents, reducing the generation of hazardous waste.
Conclusion[edit | edit source]
Supercritical fluids represent a fascinating state of matter with a wide range of practical applications in extraction, chromatography, and chemical reactions. Their unique properties offer significant advantages over traditional solvents, including enhanced efficiency, selectivity, and reduced environmental impact. As research and technology continue to evolve, the use of supercritical fluids is expected to expand, offering new solutions to industrial and environmental challenges.
| This article is a stub. You can help WikiMD by registering to expand it. |
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD