Susceptibility weighted imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging technique
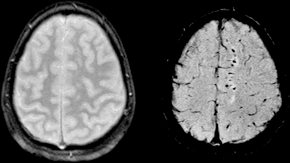
Susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI) is a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) technique that exploits the magnetic susceptibility differences of various tissues, such as blood, iron, and calcification, to generate high-contrast images. This technique is particularly useful in detecting microbleeds, venous structures, and other pathologies that may not be visible with conventional MRI sequences.
Principles[edit | edit source]
SWI is based on the principles of magnetic susceptibility, which refers to the degree to which a material can be magnetized in an external magnetic field. In SWI, the phase information from a gradient echo sequence is used to enhance the contrast of tissues with different susceptibilities. The technique involves the acquisition of both magnitude and phase images, which are then combined to produce a susceptibility-weighted image.
The phase images are particularly sensitive to the presence of paramagnetic substances such as deoxygenated blood and iron deposits. By applying a high-pass filter to the phase images, SWI can highlight these substances, providing a unique contrast that is not available in conventional MRI.
Applications[edit | edit source]
SWI is used in a variety of clinical and research settings. Some of the key applications include:
Neuroimaging[edit | edit source]
SWI is highly effective in detecting cerebral microbleeds, which are small chronic brain hemorrhages often associated with cerebral amyloid angiopathy and traumatic brain injury. It is also used to visualize venous structures and cerebral veins, which can be important in the assessment of venous thrombosis and other vascular disorders.
Trauma[edit | edit source]
In cases of traumatic brain injury, SWI can detect small hemorrhages and diffuse axonal injury that may not be visible on conventional MRI sequences. This makes it a valuable tool in the assessment of head trauma.
Neurodegenerative Diseases[edit | edit source]
SWI is used in the study of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease, where it can detect iron deposition in the brain, which is thought to play a role in the pathophysiology of these conditions.
Vascular Malformations[edit | edit source]
SWI is useful in the evaluation of vascular malformations such as cavernous hemangiomas and arteriovenous malformations. It can provide detailed information about the venous architecture and the presence of associated hemorrhages.
Other Applications[edit | edit source]
SWI is also used in the assessment of brain tumors, stroke, and multiple sclerosis. In stroke, it can help identify areas of hemorrhagic transformation. In multiple sclerosis, it can detect iron deposition in the basal ganglia and other regions.
Technique[edit | edit source]
The SWI technique involves the use of a high-resolution, three-dimensional, fully flow-compensated gradient echo sequence. The images are acquired with a long echo time to enhance the susceptibility effects. The phase images are processed to create a phase mask, which is then multiplied with the magnitude images to produce the final SWI.
Advantages and Limitations[edit | edit source]
SWI offers several advantages over conventional MRI techniques, including its ability to detect small hemorrhages and venous structures with high sensitivity. However, it also has limitations, such as susceptibility to artifacts from air-tissue interfaces and the need for specialized post-processing techniques.
Related pages[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD