Autosomal dominant cerebellar ataxia
(Redirected from Cerebellar ataxia, dominant pure)
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Autosomal dominant cerebellar ataxia | |
|---|---|

| |
| Synonyms | Spinocerebellar ataxia (SCA) |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Ataxia, dysarthria, nystagmus, tremor |
| Complications | N/A |
| Onset | Typically adulthood |
| Duration | Chronic |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Genetic mutation |
| Risks | Family history |
| Diagnosis | Genetic testing, neurological examination |
| Differential diagnosis | Multiple sclerosis, Friedreich's ataxia, ataxia-telangiectasia |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Progressive |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |
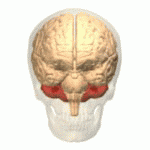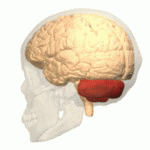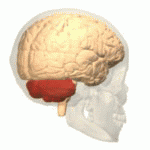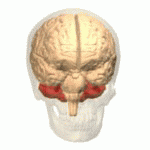
Autosomal Dominant Cerebellar Ataxia (ADCA) is a group of genetic disorders characterized by progressive degeneration of the cerebellum, the part of the brain that controls coordination and balance. These disorders vary widely in their other symptoms and age of onset, but all share the common feature of cerebellar ataxia, which includes uncoordinated movement, gait abnormalities, and problems with fine motor tasks.
Types and Genetics[edit | edit source]
ADCA is classified into several types, based on genetic cause and clinical presentation. The most common types include Spinocerebellar Ataxia (SCA), Episodic Ataxia (EA), and Dentatorubral-Pallidoluysian Atrophy (DRPLA). Each type is further subdivided into various subtypes, such as SCA1, SCA2, SCA3 (also known as Machado-Joseph Disease), and so on, based on the specific gene mutation involved. The mode of inheritance for ADCA is autosomal dominant, meaning a mutation in just one copy of the gene inherited from one parent is sufficient to cause the disorder. This also implies a 50% chance of passing the mutated gene to offspring.
Symptoms[edit | edit source]
Symptoms of ADCA can vary significantly among individuals, even within the same family. Common symptoms include:
- Difficulty with coordination and balance (ataxia)
- Slurred speech (dysarthria)
- Eye movement abnormalities
- Muscle stiffness (spasticity)
- Cognitive impairment
Symptoms typically begin in adulthood but can appear at any age, from childhood to late adulthood.
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
Diagnosis of ADCA involves a combination of clinical evaluation, family history, genetic testing, and sometimes neuroimaging studies like MRI. Genetic testing is crucial for confirming the diagnosis and identifying the specific subtype of ADCA, which can help in understanding the prognosis and, in some cases, guiding treatment.
Treatment[edit | edit source]
There is currently no cure for ADCA, and treatment is primarily supportive. It may include physical therapy to help with mobility and coordination, speech therapy, and medications to manage symptoms such as spasticity or tremor. Genetic counseling is recommended for affected individuals and their families.
Research[edit | edit source]
Research into ADCA is ongoing, with efforts focused on understanding the genetic mechanisms underlying these disorders and developing effective treatments. Gene therapy and stem cell therapy are areas of particular interest, though these are still in the experimental stages.
See Also[edit | edit source]
- Genetic disorder
- Cerebellum
- Spinocerebellar Ataxia
- Episodic Ataxia
- Dentatorubral-Pallidoluysian Atrophy
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD