Choroidal nevus
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Choroidal nevus | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Nevus of the choroid |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Usually asymptomatic, but can cause visual field defects or metamorphopsia if affecting the macula |
| Complications | Potential transformation into choroidal melanoma |
| Onset | Typically detected in adulthood |
| Duration | Lifelong |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Congenital, due to proliferation of melanocytes |
| Risks | Caucasian ethnicity, light-colored eyes, family history of melanoma |
| Diagnosis | Ophthalmoscopy, optical coherence tomography, ultrasound |
| Differential diagnosis | Choroidal melanoma, retinal detachment, age-related macular degeneration |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Observation, regular monitoring |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Generally good, low risk of malignant transformation |
| Frequency | Present in approximately 5-10% of the general population |
| Deaths | N/A |
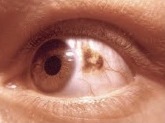
A benign pigmented growth in the eye
Choroidal Nevus[edit | edit source]
A choroidal nevus is a benign pigmented growth located in the choroid, which is the vascular layer of the eye situated between the retina and the sclera. These nevi are similar to moles on the skin and are usually asymptomatic, often discovered during routine eye examinations.
Characteristics[edit | edit source]
Choroidal nevi are typically flat or slightly elevated lesions that can vary in color from gray to brown. They are generally less than 5 mm in diameter. The presence of drusen, which are yellowish deposits, can sometimes be observed on the surface of the nevus, indicating chronicity.
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
The diagnosis of a choroidal nevus is primarily made through a comprehensive eye examination, including ophthalmoscopy and optical coherence tomography (OCT). In some cases, ultrasound imaging may be used to assess the thickness and internal reflectivity of the lesion.
Differential Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
It is crucial to differentiate a choroidal nevus from a choroidal melanoma, which is a malignant tumor. Factors that may suggest malignancy include thickness greater than 2 mm, presence of subretinal fluid, symptoms such as visual disturbances, and orange pigmentation.
Management[edit | edit source]
Most choroidal nevi do not require treatment and are simply monitored for changes over time. Regular follow-up with an eye care professional is recommended to ensure that the nevus does not exhibit signs of transformation into melanoma.
Prognosis[edit | edit source]
The prognosis for individuals with a choroidal nevus is generally excellent, as these lesions are benign and rarely transform into melanoma. However, regular monitoring is essential to detect any changes early.
See also[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD



