Erythema
(Redirected from Erythemic)
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Erythema | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Redness of the skin |
| Complications | Infection, ulceration |
| Onset | Varies depending on cause |
| Duration | Varies |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Infection, allergy, autoimmune disease, medication |
| Risks | Depends on underlying cause |
| Diagnosis | Physical examination, medical history |
| Differential diagnosis | Cellulitis, rosacea, lupus erythematosus |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Depends on underlying cause; may include antibiotics, antihistamines, corticosteroids |
| Medication | As per underlying cause |
| Prognosis | N/A |
| Frequency | Common |
| Deaths | N/A |
Erythema represents a common and visually perceptible skin condition characterized by redness or rash. This phenomenon results from the dilation and congestion of capillaries under the skin due to inflammation, infection, or an allergic reaction.
Definition and Description[edit | edit source]
Erythema is typically identified by localized redness or rash on the skin. The intensity of redness can range from light pink to a deep, dark red, depending on the underlying cause and severity. The condition may be accompanied by other symptoms such as itchiness, heat, pain, swelling, or tenderness, also contingent on the cause.
Causes and Types[edit | edit source]
There are several forms of erythema, each associated with different causes. Some of the common types include:
- Erythema multiforme: A skin reaction usually triggered by infection, particularly the herpes simplex virus, or certain medications.
- Erythema nodosum: Characterized by tender, red nodules under the skin, often linked with autoimmune diseases, infections, or pregnancy.
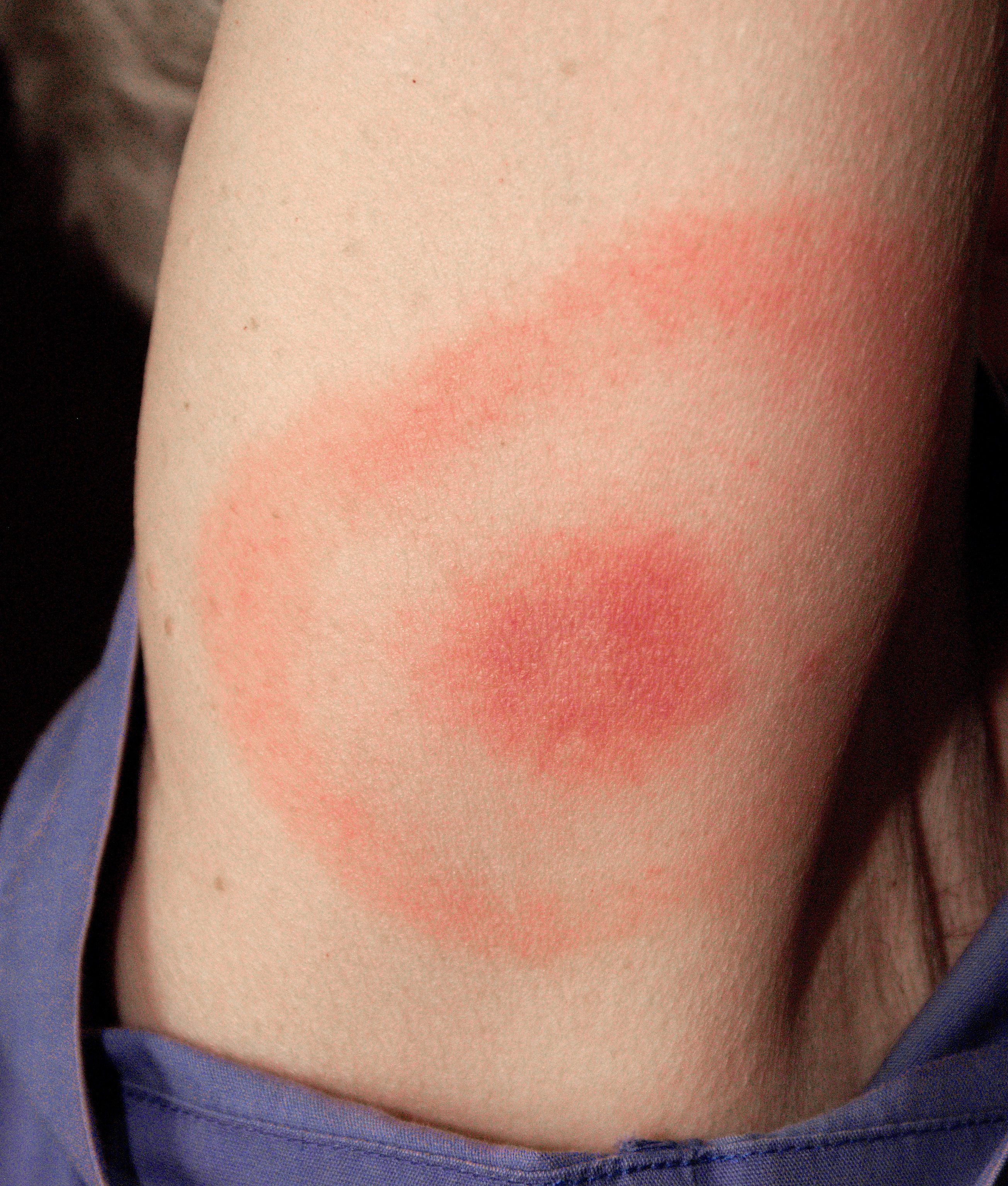
- Erythema migrans: A skin rash associated with Lyme disease that presents as a circular red rash around the site of a tick bite.
- Erythema marginatum: A ring-like rash often associated with rheumatic fever.
- Erythema infectiosum (fifth disease): A childhood illness caused by the parvovirus B19, marked by a "slapped cheek" rash.
- Erythema ab igne: Skin damage caused by chronic exposure to low levels of infrared heat, typically from heating appliances.
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
The diagnosis of erythema usually involves a physical examination of the skin. In some cases, a skin biopsy may be needed to confirm the diagnosis or rule out other conditions. Moreover, when the underlying cause is not immediately apparent, further investigations such as blood tests, allergy tests, or imaging studies may be required.
Treatment and Management[edit | edit source]
The management of erythema generally involves addressing the underlying cause. This could involve discontinuing a medication that has caused an allergic reaction, treating an underlying infection with antibiotics, or managing an autoimmune disease with immunosuppressant drugs. Topical corticosteroids, antihistamines, and soothing lotions may be recommended to alleviate the symptoms.
References[edit | edit source]
- Bolognia, J. L., Schaffer, J. V., & Cerroni, L. (2018). Dermatology. Elsevier Health Sciences.
- Cohen, B. A. (2013). Pediatric Dermatology. Elsevier Health Sciences.
- James, W. D., Berger, T. G., & Elston, D. M. (2015). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. Elsevier Health Sciences.
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD



