Roseola
(Redirected from Exanthema subitum)
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Roseola | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Sixth disease, exanthem subitum |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | High fever, rash |
| Complications | Febrile seizure |
| Onset | Usually between 6 months and 2 years of age |
| Duration | Fever lasts 3-5 days, rash lasts 1-2 days |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6) and Human herpesvirus 7 (HHV-7) |
| Risks | Immunocompromised individuals |
| Diagnosis | Clinical evaluation |
| Differential diagnosis | Measles, Rubella, Scarlet fever |
| Prevention | None |
| Treatment | Supportive care, antipyretics |
| Medication | Ibuprofen, Acetaminophen |
| Prognosis | Excellent |
| Frequency | Common in children under 2 years |
| Deaths | N/A |
Roseola (also known as exanthem subitum, sixth disease, and roseola infantum) is a clinical syndrome characterized by three days of high fever that is resolved by a rash. The disease is primarily caused by two human herpesviruses, HHV-6 and HHV-7, both of which are sometimes referred to as Roseolovirus.
Signs and Symptoms[edit | edit source]
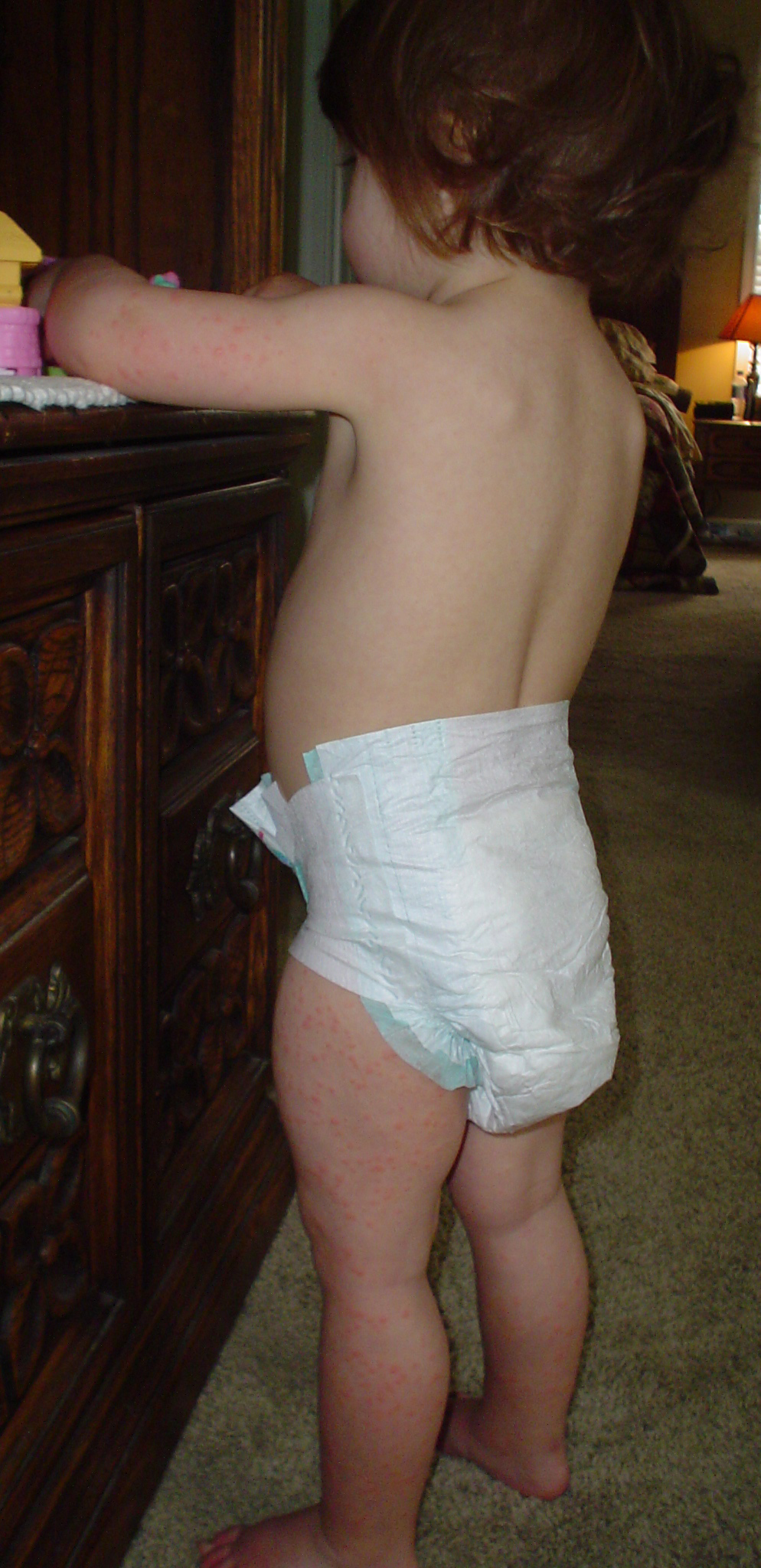
Roseola is most common in children 6 months to 2 years of age, with the average age of infection at around 9 months of age. The disease begins with a sudden high fever (39–40 ¬∞C; 102.2-104 ¬∞F). This can cause, in some cases, febrile convulsions (also known as febrile seizures or fever fits) due to the sudden rise in body temperature, but in many cases the child appears normal. After a few days the fever subsides, and just as the child appears to be recovering, a red rash appears. This usually begins on the trunk, spreading to the legs and neck. The rash is not itchy and may last 1 to 2 days. In contrast, a child suffering from measles would usually appear more ill, with symptoms of conjunctivitis and a cough, and their rash would affect the face and last for several days.
Cause[edit | edit source]
Roseola is caused by two human herpesviruses, Human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6) and Human herpesvirus 7 (HHV-7), which are sometimes referred to collectively as Roseolovirus. Other viruses can also cause roseola.
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
Roseola is typically diagnosed by the symptoms, particularly the characteristic rash. If the rash is not present, it may be difficult to diagnose since the other symptoms are common in many other diseases.
Treatment[edit | edit source]
There is no specific treatment for roseola. The disease usually gets better without treatment. However, because of the fever, it is important to prevent dehydration.
Prevention[edit | edit source]
There is no vaccine for roseola. The best prevention is good hygiene.
See also[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD


