Hibernoma
(Redirected from Fetal lipoma)
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Hibernoma | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Usually asymptomatic, may present as a painless mass |
| Complications | Rarely, compression of adjacent structures |
| Onset | Typically in adults |
| Duration | Indefinite |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Unknown |
| Risks | |
| Diagnosis | Histopathology, Imaging studies |
| Differential diagnosis | Liposarcoma, Lipoma, Myxoid liposarcoma |
| Prevention | None |
| Treatment | Surgical excision |
| Medication | None |
| Prognosis | Excellent with complete excision |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |
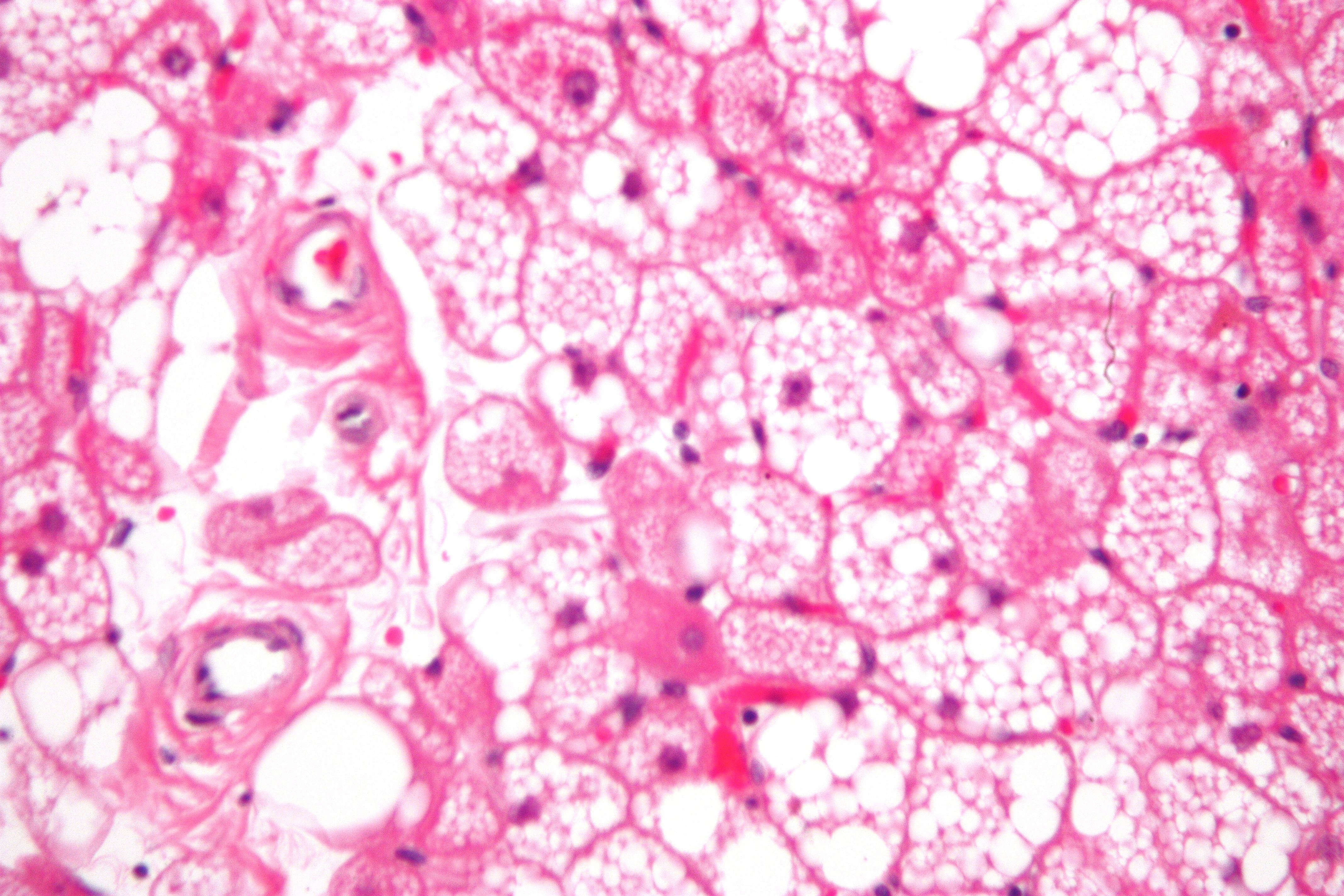
Hibernoma is a rare, benign tumor that originates from brown fat tissue. The name "hibernoma" is derived from the tumor's resemblance to the brown fat found in hibernating animals.
History[edit | edit source]
The first known case of hibernoma was reported by Merkel in 1906. Since then, fewer than 200 cases have been reported in the medical literature.
Pathology[edit | edit source]
Hibernomas are composed of brown fat cells, which are larger than white fat cells and contain more mitochondria. These cells are responsible for heat production in the body, a process known as thermogenesis.
Clinical Presentation[edit | edit source]
Patients with hibernoma often present with a slow-growing, painless mass. The most common locations for hibernomas are the thigh, shoulder, back, and neck.
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
The diagnosis of hibernoma is typically made through a combination of imaging studies and biopsy. On imaging, hibernomas appear as well-defined, vascular masses. The definitive diagnosis is made by biopsy, which shows the characteristic brown fat cells.
Treatment[edit | edit source]
The treatment for hibernoma is surgical removal. Because hibernomas are benign, they do not spread to other parts of the body, and complete removal is usually curative.
Prognosis[edit | edit source]
The prognosis for patients with hibernoma is excellent. After surgical removal, the recurrence rate is very low.
See Also[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD


