MELAS syndrome
(Redirected from MELAS)
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| MELAS syndrome | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Mitochondrial encephalomyopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episodes |
| Pronounce | |
| Specialty | Neurology, Genetics |
| Symptoms | Seizures, stroke-like episodes, muscle weakness, hearing loss, lactic acidosis |
| Complications | N/A |
| Onset | Childhood or early adulthood |
| Duration | Lifelong |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Mutations in mitochondrial DNA |
| Risks | Family history of mitochondrial disorders |
| Diagnosis | Genetic testing, muscle biopsy |
| Differential diagnosis | Stroke, multiple sclerosis, epilepsy |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Symptomatic treatment, coenzyme Q10, L-arginine |
| Medication | Anticonvulsants, lactic acid management |
| Prognosis | Variable, progressive |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | |
Mitochondrial Encephalopathy, Lactic Acidosis, and Stroke-Like Episodes (MELAS) is a rare and complex genetic disorder classified under the family of mitochondrial diseases. This group also includes conditions like MERRF syndrome (Myoclonic Epilepsy with Ragged-Red Fibers) and Leber's Hereditary Optic Neuropathy (LHON). MELAS was first characterized under this name in 1984. A hallmark of these diseases is that they result from defects in the mitochondrial genome, which is exclusively inherited from the female parent.
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Mitochondrial diseases, including MELAS, are a group of rare genetic disorders that affect the mitochondria, the cellular organelles responsible for producing energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). MELAS is characterized by a combination of symptoms, including encephalopathy (brain dysfunction), lactic acidosis (accumulation of lactic acid in the body), and stroke-like episodes.
Causes[edit | edit source]
MELAS is primarily caused by mutations in the mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA). Unlike nuclear DNA, which is inherited from both parents, mtDNA is inherited exclusively from the mother. The specific genetic mutations associated with MELAS disrupt the normal functioning of the mitochondrial respiratory chain, leading to impaired energy production within cells.
Clinical Features[edit | edit source]
The clinical presentation of MELAS is highly variable and can include the following features:
- Stroke-like episodes: One of the defining characteristics of MELAS is the occurrence of stroke-like episodes. These episodes can manifest as temporary neurological deficits, such as weakness, vision problems, and seizures, which often resemble strokes but lack the typical vascular causes.
- Lactic acidosis: Lactic acidosis is a common feature in MELAS and results from the accumulation of lactic acid in the blood. It can lead to symptoms like nausea, vomiting, muscle weakness, and rapid breathing.
- Encephalopathy: Individuals with MELAS may experience progressive neurological symptoms, including cognitive impairment, dementia, and muscle weakness.
- Migraine-Like headaches: Recurrent migraine-like headaches are also observed in many MELAS patients.
- Muscle weakness: Muscle weakness, fatigue, and exercise intolerance are common symptoms.
- Hearing loss: Sensorineural hearing loss can occur in some individuals with MELAS.
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
Diagnosing MELAS involves a combination of clinical evaluation, genetic testing, and laboratory assessments. Key diagnostic criteria include the presence of characteristic clinical features, elevated blood and cerebrospinal fluid lactate levels, and the identification of pathogenic mitochondrial DNA mutations.
Treatment[edit | edit source]
As of now, there is no cure for MELAS. Treatment primarily focuses on managing symptoms and complications. This may include medications to control seizures, physical therapy to address muscle weakness, and supportive care to address specific symptoms. Some individuals may benefit from dietary interventions aimed at reducing lactic acid production.
Research and Outlook[edit | edit source]
Ongoing research into mitochondrial diseases like MELAS aims to better understand the underlying genetic mechanisms and develop potential therapies. Mitochondrial replacement therapies, such as mitochondrial DNA replacement, are being explored as potential treatments for these conditions.
Clinical Case: (MELAS)[edit | edit source]
Patient History[edit | edit source]
- Name: Emily Johnson
- Age: 25 years
- Gender: Female
- Presenting Complaint: Recurrent neurological episodes and muscle weakness
Chief Complaint[edit | edit source]
Emily Johnson, a 25-year-old female, presents to the neurology clinic with recurrent episodes of neurological symptoms, including weakness on one side of her body, visual disturbances, and severe headaches. She reports that these episodes have been occurring for the past year and have been increasing in frequency and severity.
Past Medical History[edit | edit source]
Emily has a relatively unremarkable past medical history, with no significant illnesses or surgeries. There is no family history of similar neurological conditions. She is not taking any regular medications.
Physical Examination[edit | edit source]
- Vital Signs: Within normal limits
- Neurological Examination:
- * - During the examination, Emily experiences a transient episode of right-sided weakness and numbness, which resolves after a few minutes.
- * - Visual field examination reveals a left homonymous hemianopia (loss of vision on the left side of both visual fields).
- * - Muscle strength: Slightly reduced on the right side, with no focal motor deficits.
- * - Deep tendon reflexes: Normal
- * - Sensory examination: No sensory deficits identified
- General Examination:
- * - No signs of acute distress
- * - No abnormalities in cardiovascular, respiratory, or gastrointestinal systems
Diagnostic Evaluation[edit | edit source]
- Laboratory Investigations:
- * - Elevated blood lactate levels (4.8 mmol/L; normal range: 0.5-2.2 mmol/L)
- * - Genetic testing reveals a pathogenic mutation in mitochondrial DNA associated with MELAS syndrome.
- Imaging:
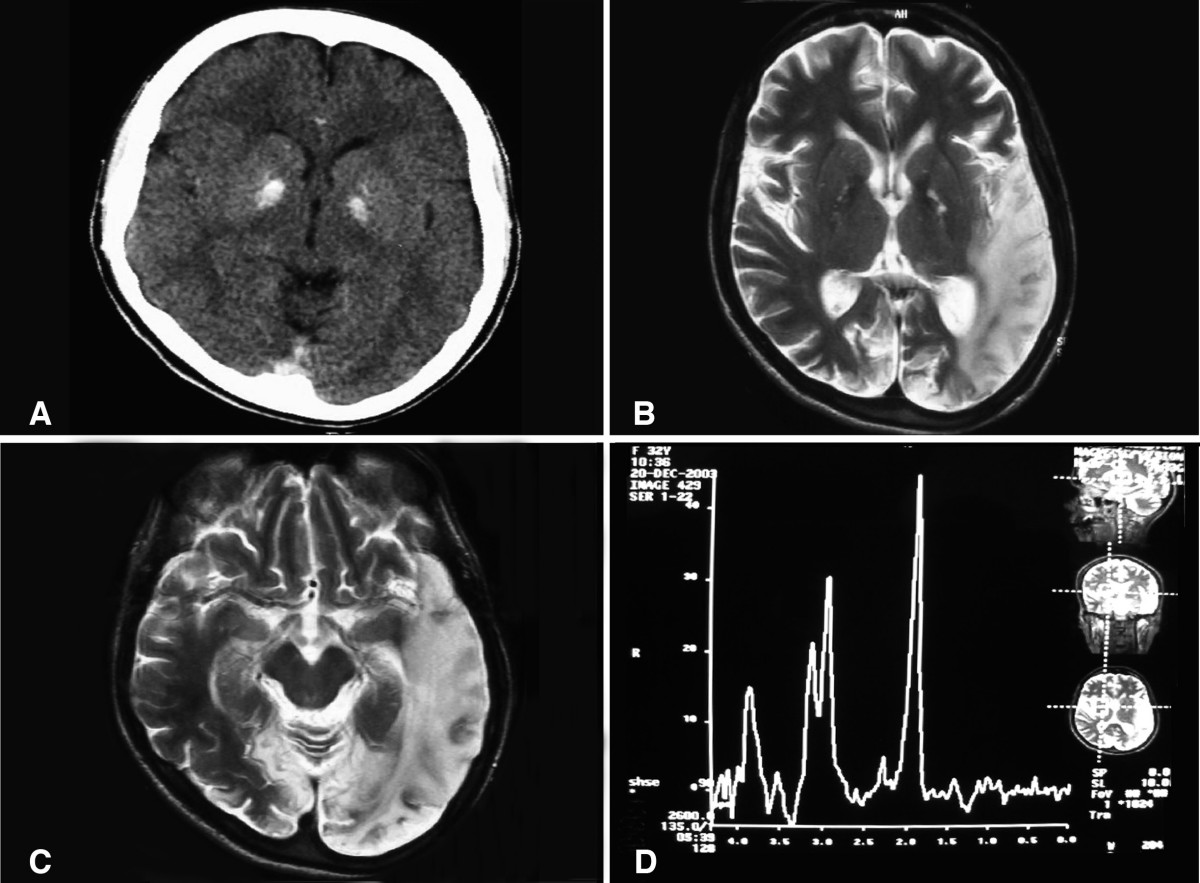
- Brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) shows characteristic findings of multiple cortical and subcortical hyperintense lesions on T2-weighted images in the left occipital lobe, consistent with previous stroke-like episodes.
- Electroencephalogram (EEG):
- *- Interictal EEG demonstrates focal epileptiform discharges in the left occipital region.
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
Based on clinical presentation, elevated lactate levels, imaging findings, and genetic testing, Emily is diagnosed with Mitochondrial Encephalopathy, Lactic Acidosis, and Stroke-Like Episodes (MELAS) syndrome.
Discussion[edit | edit source]
MELAS is a rare mitochondrial disorder caused by mutations in mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA). It primarily affects the nervous system and can lead to various neurological symptoms, including recurrent stroke-like episodes, seizures, muscle weakness, and visual disturbances. The hallmark of MELAS is the presence of elevated blood and cerebrospinal fluid lactate levels, which indicate impaired mitochondrial energy production. In Emily's case, the clinical findings, including recurrent neurological episodes, left homonymous hemianopia, and characteristic brain MRI and EEG findings, align with the diagnosis of MELAS. The pathogenic mtDNA mutation identified in genetic testing confirms the diagnosis. Management of MELAS typically involves symptom-specific treatments, including antiepileptic medications for seizures, supportive care for muscle weakness, and monitoring for stroke-like episodes. While there is currently no cure for MELAS, ongoing research into mitochondrial diseases offers hope for potential future treatments. This case highlights the importance of considering mitochondrial disorders like MELAS in patients presenting with unexplained neurological symptoms, especially when accompanied by elevated lactate levels and suggestive imaging findings.
See Also[edit | edit source]
| This article is a medical stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it! | |
|---|---|
NIH genetic and rare disease info[edit source]
MELAS syndrome is a rare disease.
| Rare and genetic diseases | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Rare diseases - MELAS syndrome
|
| Mitochondrial diseases | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
see also mitochondrial proteins
|
| Diseases of muscle, neuromuscular junction, and neuromuscular disease | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's NYC physician weight loss.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available. Call 718 946 5500.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD


