Clear cell sarcoma
(Redirected from Melanoma of the soft parts)
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Clear cell sarcoma | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Malignant melanoma of soft parts |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Lump, pain, tenderness |
| Complications | Metastasis |
| Onset | Young adults |
| Duration | Long-term |
| Types | |
| Causes | Unknown |
| Risks | |
| Diagnosis | Biopsy, Immunohistochemistry |
| Differential diagnosis | Melanoma, Synovial sarcoma |
| Prevention | |
| Treatment | Surgery, Radiation therapy, Chemotherapy |
| Medication | |
| Prognosis | Variable, often poor |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |
Clear Cell Sarcoma[edit | edit source]
Clear cell sarcoma is a rare type of soft tissue sarcoma that is often associated with tendons and aponeuroses. It is sometimes referred to as "malignant melanoma of soft parts" due to its histological and immunohistochemical similarities to melanoma.
Pathophysiology[edit | edit source]
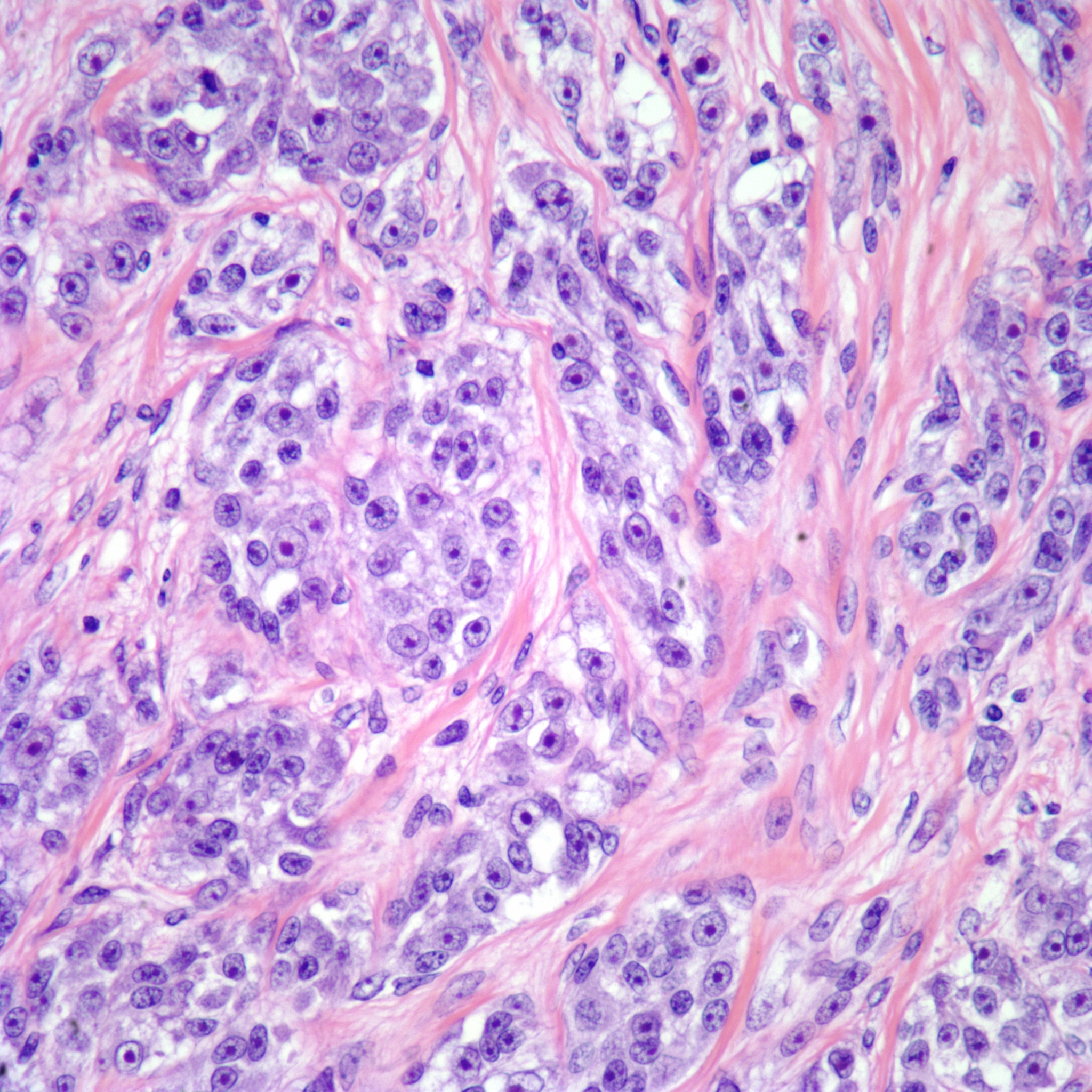
Clear cell sarcoma is characterized by the presence of clear cells, which are so named because of their pale, clear cytoplasm when viewed under a microscope. This appearance is due to the presence of glycogen within the cells. The tumor cells typically form nests and are surrounded by fibrous septa. A defining feature of clear cell sarcoma is the presence of a specific chromosomal translocation, t(12;22)(q13;q12), which results in the fusion of the EWSR1 gene on chromosome 22 with the ATF1 gene on chromosome 12. This genetic alteration is a key diagnostic marker and plays a role in the pathogenesis of the disease.
Clinical Presentation[edit | edit source]
Patients with clear cell sarcoma often present with a slow-growing mass that is typically located in the extremities, particularly the lower limbs. The tumor is usually deep-seated and may be associated with pain or tenderness. Due to its indolent nature, the diagnosis is often delayed.
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
The diagnosis of clear cell sarcoma is based on a combination of clinical, radiological, and histopathological findings. Imaging studies such as MRI and CT scan are used to assess the extent of the tumor. A biopsy is necessary to obtain tissue for histological examination. Histologically, clear cell sarcoma is composed of nests of uniform, round to oval cells with clear cytoplasm and prominent nucleoli. Immunohistochemical staining is positive for markers such as S-100 protein, HMB-45, and Melan-A, which are also seen in melanoma.
Treatment[edit | edit source]
The primary treatment for clear cell sarcoma is surgical resection with wide margins to ensure complete removal of the tumor. Due to the high risk of local recurrence and metastasis, adjuvant therapies such as radiation therapy and chemotherapy may be considered, although their effectiveness is limited.
Prognosis[edit | edit source]
Clear cell sarcoma has a poor prognosis due to its aggressive nature and tendency to metastasize, particularly to the lungs and regional lymph nodes. The 5-year survival rate is approximately 50%, and long-term follow-up is necessary to monitor for recurrence and metastasis.
See also[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD

