Monoamine nuclei
Clusters of neurons in the brainstem that produce monoamines
Monoamine nuclei are clusters of neurons located in the brainstem that are responsible for the production and release of monoamine neurotransmitters. These neurotransmitters include serotonin, dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine. The monoamine nuclei play a crucial role in regulating mood, arousal, and various autonomic functions.
Anatomy and Function[edit | edit source]
The monoamine nuclei are primarily located in the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata. They are organized into several distinct groups, each associated with the production of specific monoamines.
Raphe Nuclei[edit | edit source]
The raphe nuclei are a group of nuclei located along the midline of the brainstem. They are the primary source of serotonin in the brain. The raphe nuclei are involved in the regulation of mood, anxiety, and sleep. They project to various regions of the brain, including the cerebral cortex, hippocampus, and amygdala.
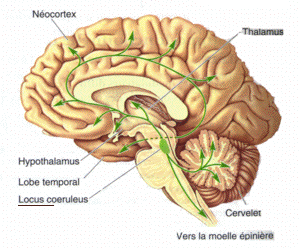
Locus Coeruleus[edit | edit source]
The locus coeruleus is a small nucleus located in the pons. It is the principal site for the synthesis of norepinephrine in the brain. The locus coeruleus is involved in the regulation of attention, arousal, and the sleep-wake cycle. It projects to numerous areas of the brain, including the cerebellum, thalamus, and spinal cord.
Substantia Nigra[edit | edit source]
The substantia nigra is located in the midbrain and is divided into two parts: the pars compacta and the pars reticulata. The pars compacta is rich in dopamine-producing neurons and plays a critical role in the regulation of movement. Dysfunction of the substantia nigra is associated with Parkinson's disease.
Ventral Tegmental Area[edit | edit source]
The ventral tegmental area (VTA) is another dopaminergic nucleus located in the midbrain. It is involved in the reward circuitry of the brain and is implicated in the regulation of motivation and pleasure. The VTA projects to the nucleus accumbens, prefrontal cortex, and other limbic structures.
Other Monoamine Nuclei[edit | edit source]
Other important monoamine nuclei include the nucleus of the solitary tract, which is involved in autonomic control, and the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus nerve, which plays a role in parasympathetic regulation.
Physiological Roles[edit | edit source]
Monoamine nuclei are essential for maintaining homeostasis and regulating various physiological processes. They influence mood, cognition, and behavior through their widespread projections and the release of monoamines.
Mood and Emotion[edit | edit source]
Monoamines such as serotonin and dopamine are critical in the regulation of mood and emotion. Imbalances in these neurotransmitters are associated with mood disorders such as depression and anxiety.
Arousal and Sleep[edit | edit source]
The locus coeruleus and raphe nuclei are involved in the regulation of the sleep-wake cycle and arousal. Norepinephrine and serotonin levels fluctuate during different stages of sleep and wakefulness.
Autonomic Functions[edit | edit source]
Monoamine nuclei also play a role in autonomic functions such as heart rate, blood pressure, and digestion. The nucleus of the solitary tract and the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus nerve are particularly important in these processes.
Clinical Significance[edit | edit source]
Dysfunction of monoamine nuclei is implicated in various neurological and psychiatric disorders. For example, degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra leads to Parkinson's disease, while alterations in serotonergic and noradrenergic systems are linked to depression and anxiety disorders.
Related Pages[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's NYC physician weight loss.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available. Call 718 946 5500.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD