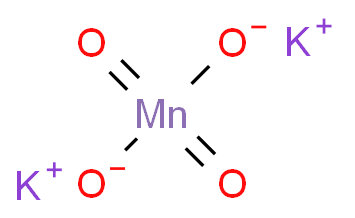
Potassium manganate
Potassium manganate is the inorganic compound with the formula K2MnO4. This green-colored salt is an intermediate in the industrial synthesis of potassium permanganate (KMnO4), a common chemical used in laboratories and in various industrial applications. Potassium manganate is a strong oxidizing agent and is used in quantitative analysis and in medicine.
Properties[edit | edit source]
Potassium manganate is a green solid that is soluble in water, producing a green solution. It is stable in alkaline solutions but decomposes in acidic solutions to manganese dioxide (MnO2) and oxygen (O2). The compound is a strong oxidizing agent and can cause fires upon contact with organic materials or reducing agents.
Synthesis[edit | edit source]
Potassium manganate is typically synthesized by the oxidation of manganese dioxide (MnO2) with potassium hydroxide (KOH) and oxygen (O2) at high temperatures. This process also produces potassium manganate(VII) (KMnO4), and the mixture can be separated by fractional crystallization.
Applications[edit | edit source]
Potassium manganate is primarily used as an intermediate in the production of potassium permanganate, a compound with widespread applications in organic chemistry, disinfection, and water treatment. It is also used in analytical chemistry as an oxidizing agent in various types of titrations.
Health and Safety[edit | edit source]
As a strong oxidizing agent, potassium manganate can cause fires and explosions when in contact with organic materials or reducing agents. It is also harmful if swallowed, inhaled, or comes in contact with skin. Appropriate safety measures, including the use of personal protective equipment, are essential when handling this compound.
See also[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD