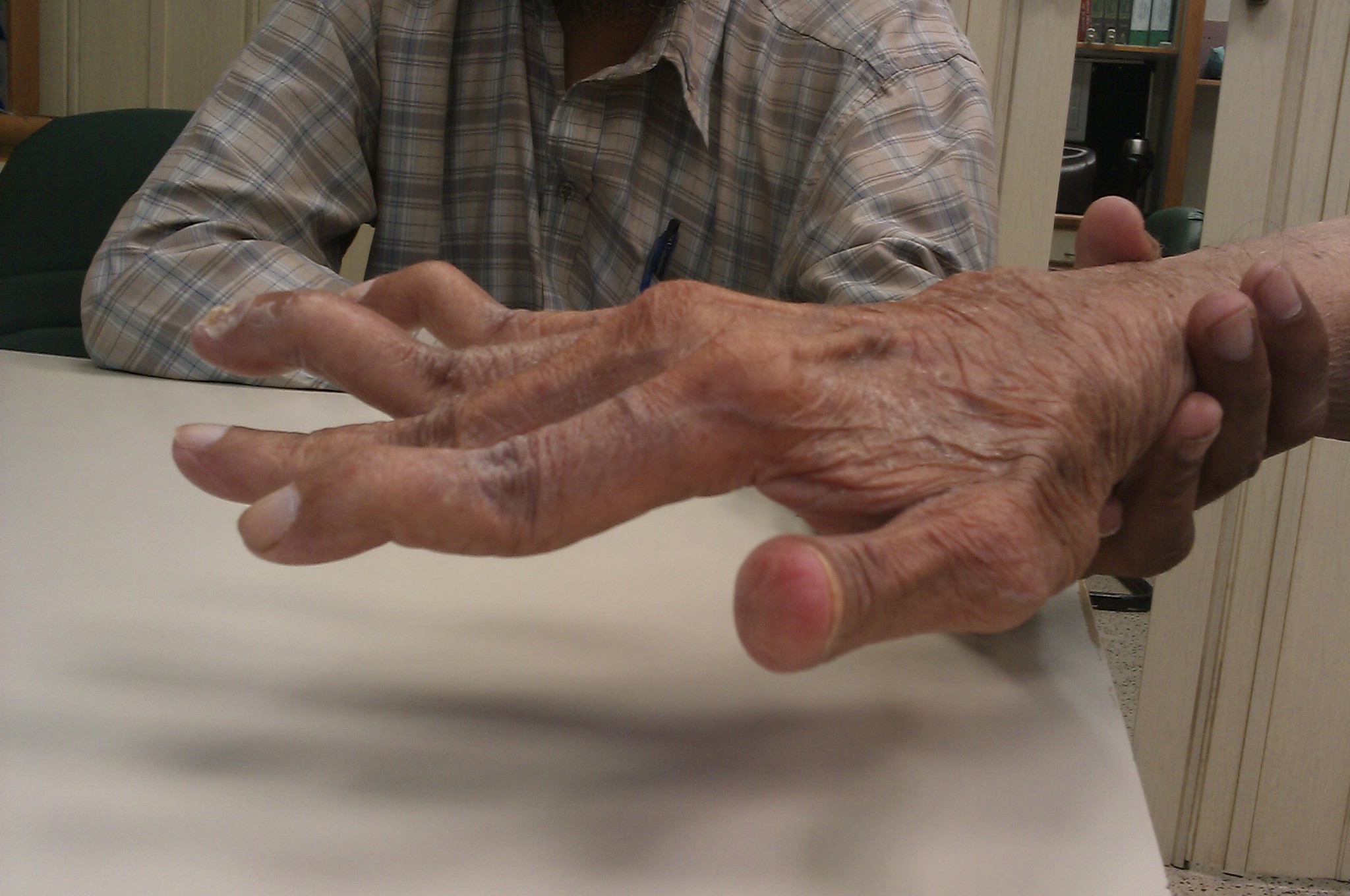
Swan neck deformity
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Swan neck deformity | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Hyperextension of the proximal interphalangeal joint and flexion of the distal interphalangeal joint |
| Complications | Functional impairment, pain |
| Onset | Gradual |
| Duration | Chronic |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Rheumatoid arthritis, trauma, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, cerebral palsy |
| Risks | Joint laxity, inflammatory arthritis |
| Diagnosis | Physical examination, X-ray |
| Differential diagnosis | Boutonniere deformity, mallet finger |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Splinting, physical therapy, surgery |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Variable, depending on underlying cause and treatment |
| Frequency | Common in rheumatoid arthritis patients |
| Deaths | N/A |
Swan Neck Deformity[edit | edit source]
Swan Neck Deformity is a condition characterized by the flexion of the distal interphalangeal joint (DIP) and hyperextension of the proximal interphalangeal joint (PIP) of the fingers, giving the finger a shape reminiscent of a swan's neck. This condition can significantly affect hand function and aesthetics.
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Swan Neck Deformity is often associated with rheumatic diseases, such as Rheumatoid Arthritis, but can also result from trauma, ligament laxity, or congenital conditions. The deformity arises from an imbalance in the tendons and ligaments that control finger movements, leading to the characteristic finger posture.
Causes[edit | edit source]
The primary causes of Swan Neck Deformity include:
- Rheumatoid arthritis which causes inflammation and changes in the joints and ligaments.
- Traumatic injuries to the fingers that affect the ligaments.
- Congenital conditions present at birth.
- Neuromuscular diseases that affect the balance of muscle forces around the joints.
Symptoms[edit | edit source]
Symptoms of Swan Neck Deformity may include:
- Difficulty in bending the finger at the affected joint.
- Pain and discomfort in the finger, especially when trying to flex.
- Cosmetic concerns due to the appearance of the finger.
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
Diagnosis of Swan Neck Deformity involves a physical examination by a healthcare provider, who may also request imaging tests, such as X-rays, to assess the extent of the deformity and rule out other conditions.
Treatment[edit | edit source]
Treatment options vary based on the severity of the deformity and the underlying cause, including:
- Non-surgical treatments such as splinting, to help realign the finger joints and reduce the deformity.
- Occupational or physical therapy to strengthen the muscles and improve joint function.
- Surgical intervention in severe cases to correct the deformity, which may involve tendon transfers, joint fusion, or other procedures.
Prevention and Management[edit | edit source]
While it may not always be possible to prevent Swan Neck Deformity, especially in cases related to genetic conditions, managing underlying diseases like rheumatoid arthritis can minimize the risk of developing the deformity. Regular follow-up with healthcare providers and adherence to treatment plans are crucial.
External Links[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Kondreddy Naveen, Prab R. Tumpati, MD


