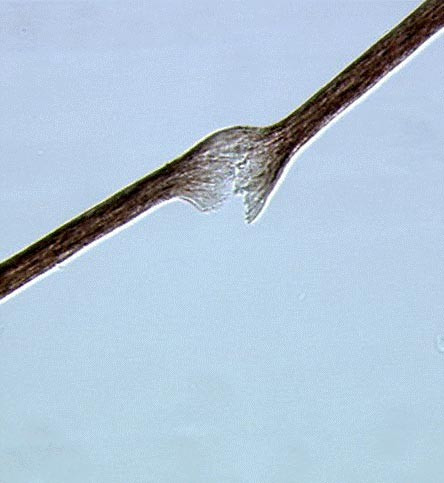
Trichorrhexis nodosa
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Trichorrhexis nodosa | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Knotted hair |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Hair breakage, hair fragility |
| Complications | Hair loss |
| Onset | Childhood or adulthood |
| Duration | Chronic |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Genetic disorder, physical trauma, chemical exposure |
| Risks | Excessive hair styling, chemical treatments |
| Diagnosis | Clinical examination, trichoscopy |
| Differential diagnosis | Monilethrix, pili torti, trichothiodystrophy |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Avoidance of trauma, gentle hair care, moisturizing treatments |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Good with proper care |
| Frequency | Common |
| Deaths | N/A |
A hair shaft disorder
Trichorrhexis nodosa is a condition that affects the hair shaft, leading to hair breakage and the appearance of white nodules along the hair strand. It is a common cause of hair fragility and can be either acquired or congenital.
Presentation[edit | edit source]
Trichorrhexis nodosa is characterized by the presence of nodes or swellings along the hair shaft. These nodes are weak points where the hair is prone to breakage. The condition can affect any hair-bearing area of the body, but it is most commonly observed on the scalp.
Symptoms[edit | edit source]
Individuals with trichorrhexis nodosa may notice:
- Brittle hair that breaks easily
- White nodules along the hair shaft
- Hair that appears frizzy or lacks shine
Causes[edit | edit source]
Trichorrhexis nodosa can be caused by:
- Physical trauma to the hair, such as excessive brushing or styling
- Chemical damage from hair treatments like bleaching or perming
- Genetic factors, in the case of congenital trichorrhexis nodosa
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
Diagnosis of trichorrhexis nodosa is typically made through clinical examination and microscopic analysis of the hair. Under a microscope, the hair shaft will show characteristic nodes and fractures.
Management[edit | edit source]
Management of trichorrhexis nodosa involves addressing the underlying cause and minimizing further damage to the hair. Recommendations may include:
- Reducing physical and chemical trauma to the hair
- Using gentle hair care products
- Ensuring adequate nutrition to support hair health
Related conditions[edit | edit source]
Trichorrhexis nodosa can be associated with other conditions, such as:
See also[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
External links[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD

