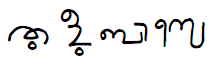Tulu language
[[file:_Tuḷu_bāse>|thumb|right]]
Tulu language
Tulu is a Dravidian language spoken by around 2 million people in the Tulu Nadu region, which comprises parts of the Karnataka and Kerala states in India. It is one of the oldest languages of the Dravidian family and has a rich oral tradition.
Geographic Distribution[edit | edit source]
Tulu is predominantly spoken in the coastal districts of Dakshina Kannada and Udupi in Karnataka, and the northern part of the Kasaragod district in Kerala. The region where Tulu is spoken is often referred to as Tulu Nadu.
History[edit | edit source]
The history of the Tulu language dates back to at least 2000 years. The earliest known inscriptions in Tulu are from the 15th century, but the language itself is believed to be much older. Tulu has a rich tradition of oral literature, including folk songs, proverbs, and folktales.
Dialects[edit | edit source]
Tulu has several dialects, which can be broadly classified into two categories: the northern dialect spoken in the Udupi and Dakshina Kannada districts, and the southern dialect spoken in the Kasaragod district. These dialects have minor variations in pronunciation and vocabulary.
Phonology[edit | edit source]
Tulu has a complex phonological system with a variety of vowels and consonants. It includes both short and long vowels, and a range of consonants including retroflex, dental, and alveolar sounds.
Grammar[edit | edit source]
Tulu grammar is typical of Dravidian languages, with a subject-object-verb (SOV) word order. It has a rich system of inflection for nouns and verbs, and uses postpositions rather than prepositions.
Writing System[edit | edit source]
Historically, Tulu was written using the Tigalari script, which is closely related to the Grantha script. However, in modern times, Tulu is most commonly written using the Kannada script.
Literature[edit | edit source]
Tulu has a rich tradition of oral literature, including epic poetry, ballads, and folktales. Written literature in Tulu is relatively recent, with the first Tulu book, "Sri Bhagavato," being published in 1842. Modern Tulu literature includes novels, short stories, and plays.
Culture[edit | edit source]
The Tulu-speaking community has a rich cultural heritage, including unique traditions, festivals, and rituals. The Yakshagana dance-drama is a notable cultural expression of the Tulu people.
Current Status[edit | edit source]
Tulu is not an officially recognized language in India, but there have been ongoing efforts to include it in the Eighth Schedule to the Constitution of India. Despite this, Tulu is actively spoken and has a vibrant community of speakers.
See Also[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
External Links[edit | edit source]
This article is a Dravidian languages-related stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD