3D rendering
3D rendering
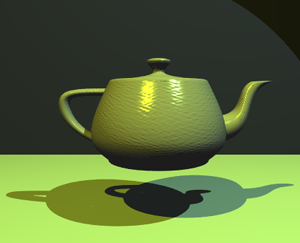
3D rendering is the process of converting 3D models into 2D images on a computer. This process is essential in various fields such as architecture, video games, film production, simulation, and virtual reality. The resulting images can be either static or animated, depending on the requirements of the project.
Process[edit | edit source]
The 3D rendering process involves several steps:
1. **Modeling**: Creating the 3D objects using 3D modeling software. This step involves defining the shape, size, and structure of the objects. 2. **Texturing**: Applying textures to the 3D models to give them color and detail. This can include bump mapping, normal mapping, and displacement mapping. 3. **Lighting**: Setting up light sources to illuminate the scene. This can include ambient lighting, point lighting, directional lighting, and spot lighting. 4. **Rendering**: The actual process of generating the 2D image from the 3D scene. This can be done using various rendering techniques such as ray tracing, rasterization, and path tracing. 5. **Post-processing**: Enhancing the rendered image with effects like bloom, depth of field, and motion blur.
Techniques[edit | edit source]
There are several techniques used in 3D rendering:
- **Ray Tracing**: A technique that simulates the way light interacts with objects to produce highly realistic images. It traces the path of light rays as they travel through the scene.
- **Rasterization**: A technique that converts 3D models into a 2D image by projecting them onto a screen. It is commonly used in real-time applications like video games.
- **Path Tracing**: An advanced form of ray tracing that simulates the global illumination of a scene by tracing the paths of many light rays.
Applications[edit | edit source]
3D rendering is used in various applications:
- **Architecture**: Creating realistic visualizations of buildings and structures before they are built.
- **Video Games**: Rendering real-time graphics for interactive gameplay.
- **Film Production**: Generating special effects and animated sequences.
- **Simulation**: Creating realistic environments for training and research.
- **Virtual Reality**: Rendering immersive 3D environments for VR experiences.
Software[edit | edit source]
Several software packages are commonly used for 3D rendering:
See Also[edit | edit source]
- 3D computer graphics
- Computer-generated imagery
- Rendering (computer graphics)
- Shading
- Texture mapping
- Global illumination
References[edit | edit source]
External Links[edit | edit source]
This article is a computer graphics–related stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD