Imperforate anus
(Redirected from Anorectal malformations)
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Imperforate anus | |
|---|---|
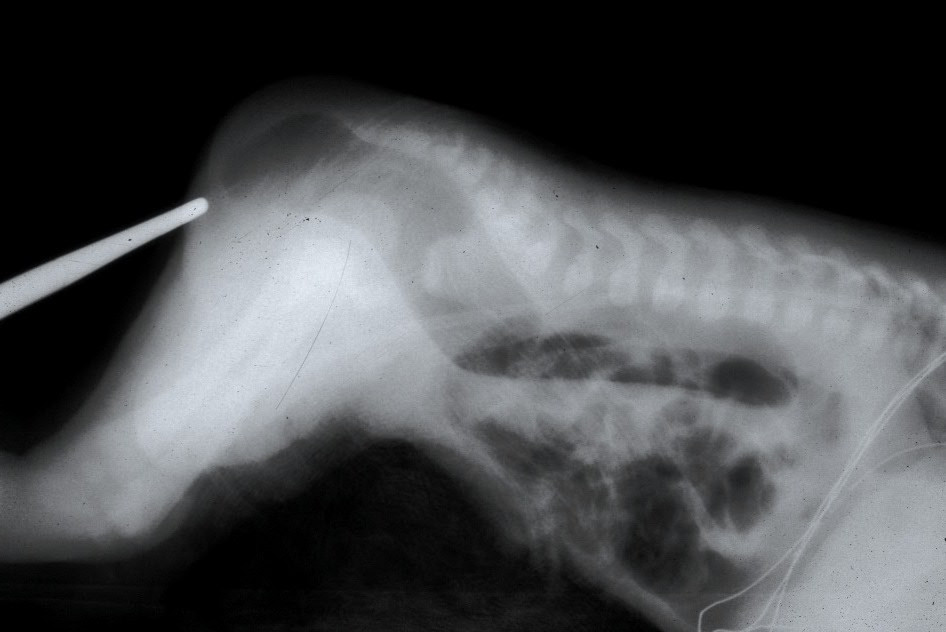
| |
| Synonyms | Anorectal malformation |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Absence of a normal anal opening, abnormal location of the anal opening, stool passing through other openings |
| Complications | Urinary tract infection, bowel obstruction, fecal incontinence |
| Onset | Congenital |
| Duration | Lifelong (with varying degrees of management) |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Congenital malformation |
| Risks | Genetic syndromes, maternal diabetes, environmental factors |
| Diagnosis | Physical examination, imaging studies |
| Differential diagnosis | Hirschsprung's disease, anal stenosis |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Surgical intervention, colostomy |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Varies depending on severity and associated anomalies |
| Frequency | 1 in 5,000 live births |
| Deaths | N/A |
Imperforate anus is a birth defect that affects about one in every 5,000 newborns, in which the rectum is malformed. The rectum is the end of the digestive system, where stool exits the body. In babies with imperforate anus, the rectum does not connect to the anus.
Causes[edit | edit source]
The exact cause of imperforate anus is unknown. It is thought to occur early in fetal development. Some studies suggest that it may be related to genetic factors, but more research is needed to confirm this.
Symptoms[edit | edit source]
The main symptom of imperforate anus is the absence of a normal rectal opening. Other symptoms can include:
- Abdominal swelling
- Failure to pass stool within the first 48 hours of life
- Unusual stooling patterns, such as passing stool from the urethra in boys or the vagina in girls
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
Imperforate anus is usually diagnosed shortly after birth during a physical examination. Additional tests may be needed to determine the severity of the condition and to check for associated anomalies. These can include:
Treatment[edit | edit source]
Treatment for imperforate anus usually involves surgery to create a new rectal opening. The type of surgery depends on the severity of the condition and the presence of associated anomalies. Some children may need additional surgeries or treatments as they grow.
Prognosis[edit | edit source]
With early diagnosis and treatment, most children with imperforate anus can lead normal lives. However, they may have ongoing issues with bowel control and may need long-term follow-up care.
See also[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD

