Diabetic retinopathy
(Redirected from Diabetic eye disease)
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Diabetic retinopathy | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Floaters, blurry vision, dark areas of vision, difficulty perceiving colors |
| Complications | Blindness, retinal detachment |
| Onset | Gradual |
| Duration | Long term |
| Types | Non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy, proliferative diabetic retinopathy |
| Causes | Diabetes mellitus |
| Risks | Poor blood sugar control, hypertension, high cholesterol, smoking |
| Diagnosis | Eye examination, fundus photography, optical coherence tomography |
| Differential diagnosis | Hypertensive retinopathy, retinal vein occlusion |
| Prevention | Blood sugar control, blood pressure control, regular eye exams |
| Treatment | Laser photocoagulation, anti-VEGF therapy, vitrectomy |
| Medication | Anti-VEGF drugs |
| Prognosis | Variable, can lead to vision loss if untreated |
| Frequency | Common in people with diabetes |
| Deaths | N/A |
Diabetic retinopathy is a diabetes-related eye condition that affects the retina. It is a serious sight-threatening complication of diabetes.
Introduction[edit | edit source]
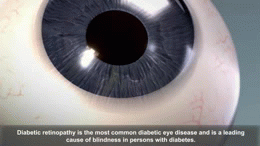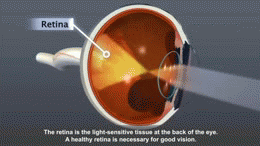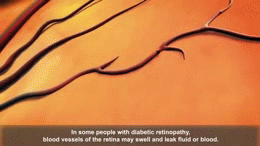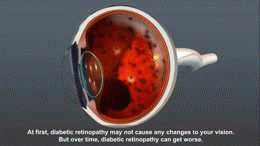
Diabetes is a chronic condition that is characterized by high blood sugar levels. Over time, these high levels can cause damage to various parts of the body, including the retina, which is the light-sensitive layer at the back of the eye. This damage is known as diabetic retinopathy.
Symptoms[edit | edit source]
In the early stages, diabetic retinopathy may cause no symptoms or only mild vision problems. However, as the condition progresses, it can lead to blindness. Symptoms can include:
- Blurred vision
- Fluctuating vision
- Dark or empty areas in your vision
- Difficulty seeing at night
- Spots or dark strings floating in your vision (floaters)
- Vision loss
Causes[edit | edit source]
Diabetic retinopathy is caused by damage to the blood vessels in the retina. This damage can occur as a result of high blood sugar levels, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and tobacco use.
Treatment[edit | edit source]
Treatment for diabetic retinopathy depends on the stage of the disease and the specific problems that need to be addressed. Options may include:
- Laser treatment
- Injection of medication into the eye
- Surgery
Prevention[edit | edit source]
The best way to prevent diabetic retinopathy is to manage your diabetes well. This includes:
- Controlling your blood sugar levels
- Controlling your blood pressure
- Controlling your cholesterol levels
- Quitting smoking
See also[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Kondreddy Naveen, Prab R. Tumpati, MD