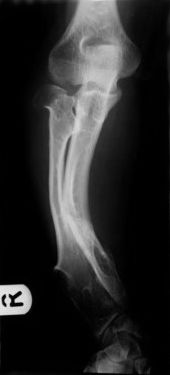
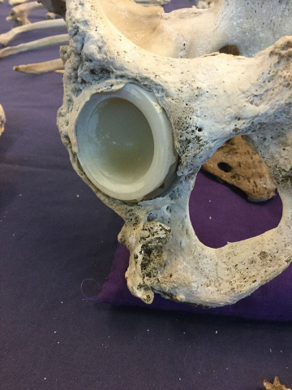
Hereditary multiple exostoses
(Redirected from Diaphyseal aclasis)
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Hereditary multiple exostoses | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Diaphyseal aclasis, Multiple osteochondromas |
| Pronounce | |
| Specialty | Orthopedics, Genetics |
| Symptoms | Multiple bony growths, limb deformities, restricted movement |
| Complications | Malignant transformation, nerve compression |
| Onset | Childhood |
| Duration | Lifelong |
| Types | |
| Causes | Genetic mutation in EXT1, EXT2, or EXT3 genes |
| Risks | Family history |
| Diagnosis | Clinical examination, X-ray, Genetic testing |
| Differential diagnosis | Ollier disease, Metachondromatosis |
| Prevention | None |
| Treatment | Surgery for symptomatic lesions |
| Medication | Pain management |
| Prognosis | Generally good, but risk of complications |
| Frequency | 1 in 50,000 |
| Deaths | Rare |
Hereditary multiple exostoses (HME) is a medical condition characterized by the development of multiple benign (non-cancerous) bone tumors known as exostoses. This condition is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, meaning that an affected person has a 50% chance of passing the disorder to each of their children.
Symptoms[edit | edit source]
The most common symptom of HME is the presence of multiple exostoses, which are often noticeable by early childhood. These exostoses can cause a variety of complications, including skeletal deformities, limited range of motion, and occasional pain. In rare cases, an exostosis may become malignant (cancerous).
Causes[edit | edit source]
HME is caused by mutations in one of two genes: EXT1 or EXT2. These genes are involved in the formation of heparan sulfate, a molecule that plays a critical role in the development and growth of bones.
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
The diagnosis of HME is typically based on the presence of multiple exostoses. Genetic testing can confirm the diagnosis and identify the specific gene mutation causing the condition.
Treatment[edit | edit source]
There is currently no cure for HME. Treatment is focused on managing symptoms and may include surgery to remove exostoses that are causing complications.
Prognosis[edit | edit source]
The prognosis for individuals with HME varies. Most people with the condition have a normal lifespan, but complications such as malignant transformation of an exostosis can affect prognosis.
See also[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD