Endocrine disease
(Redirected from Endocrinopathies)
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Endocrine disease | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Varies depending on the specific condition; may include fatigue, weight changes, mood swings, and more |
| Complications | Diabetes mellitus, thyroid disorders, adrenal insufficiency, osteoporosis, infertility |
| Onset | Can occur at any age, depending on the specific condition |
| Duration | Chronic, often lifelong |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Genetic factors, autoimmune disorders, tumors, infections, and other underlying health conditions |
| Risks | Family history, lifestyle factors, exposure to certain chemicals |
| Diagnosis | Blood test, imaging studies, biopsy, hormone level testing |
| Differential diagnosis | N/A |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Hormone replacement therapy, medication, surgery, lifestyle changes |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Varies; many conditions are manageable with treatment |
| Frequency | Common; varies by specific condition |
| Deaths | N/A |
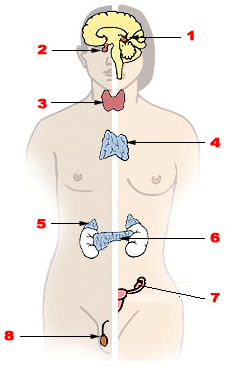
Endocrine disease refers to a wide range of conditions that affect the endocrine system, a network of glands that produce and release hormones that help control many important body functions. These diseases can be due to a problem with the endocrine glands themselves, or the levels of hormones in the body.
Introduction[edit | edit source]
The endocrine system is a complex network of glands and organs that produce, store, and secrete hormones. Hormones are your body's chemical messengers, traveling in your bloodstream to tissues or organs. They work slowly, over time, and affect many different processes, including metabolism, growth and development, sexual function, reproduction, and mood. Endocrine diseases are common and usually occur when glands produce an incorrect amount of hormones. Too much or too little of a certain hormone in the body can cause various health problems.
Types of Endocrine Diseases[edit | edit source]
There are many different types of endocrine diseases. Some of the most common include:
- Diabetes: The most common endocrine disease in the U.S. It occurs when the body fails to properly use or produce insulin.
- Thyroid diseases: These can occur when the thyroid gland produces either too much or too little thyroid hormones.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome: This condition is characterized by an imbalance in a woman's female sex hormones.
- Addison's disease: A disorder that occurs when the adrenal glands do not produce enough of their hormones.
- Cushing's disease: This condition is caused by an overproduction of the hormone cortisol by the adrenal glands.
Symptoms[edit | edit source]
The symptoms of endocrine diseases can vary greatly depending on the specific disease. However, common symptoms include:
- Fatigue
- Mood changes
- Skin rash
- Weight gain or weight loss
- Increased thirst and urination
Diagnosis and Treatment[edit | edit source]
Diagnosis of endocrine diseases often involves blood tests to measure hormone levels. Imaging tests may also be used to check for any abnormalities in the glands. Treatment typically involves managing the symptoms and correcting the hormone imbalance. This may involve hormone replacement therapy, medications, lifestyle changes, or in some cases, surgery.
See Also[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD


