Methanobacteriati
(Redirected from Euryarchaeota)
Methanobacteriaceae[edit | edit source]
The Methanobacteriaceae are a family of archaea within the order Methanobacteriales. These microorganisms are known for their ability to produce methane as a metabolic byproduct in anoxic conditions. They are a significant component of the methanogenic archaea, which play a crucial role in the carbon cycle by converting carbon dioxide and hydrogen into methane.
Characteristics[edit | edit source]
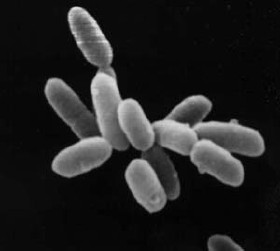
Methanobacteriaceae are characterized by their rod-shaped morphology and their ability to thrive in anaerobic environments. They are obligate anaerobes, meaning they cannot survive in the presence of oxygen. These archaea possess a unique cell wall structure that lacks peptidoglycan, which is typical of bacteria. Instead, their cell walls are composed of pseudopeptidoglycan, which provides structural integrity and protection.
The members of this family are typically found in environments such as wetlands, rice paddies, and the digestive tracts of ruminants and other animals. They are also present in anaerobic digesters used for waste treatment.
Metabolism[edit | edit source]
Methanobacteriaceae are methanogens, meaning they produce methane through a process known as methanogenesis. This process involves the reduction of carbon compounds, such as carbon dioxide, using hydrogen as an electron donor. The overall reaction can be summarized as:
- CO₂ + 4 H₂ → CH₄ + 2 H₂O
This metabolic pathway is crucial for the global carbon cycle, as it helps in the decomposition of organic matter in anaerobic environments.
Ecological Importance[edit | edit source]
The Methanobacteriaceae play a vital role in the biogeochemical cycles of carbon and hydrogen. By converting carbon dioxide and hydrogen into methane, they help in reducing greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. However, methane itself is a potent greenhouse gas, and the activity of methanogens contributes to its levels in the atmosphere.
In agricultural settings, such as rice paddies and livestock farming, methanogens are responsible for a significant portion of methane emissions. Understanding their ecology and metabolism is essential for developing strategies to mitigate methane emissions and address climate change.
Related Pages[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD