HLA-B7
HLA-B7 is a human leukocyte antigen (HLA) serotype within the HLA-B locus. The serotype identifies the gene products (proteins) of the HLA-B*07 allele group. HLA-B7 is one of the most common HLA-B alleles in many populations and has been extensively studied in relation to its role in the immune system and its association with various diseases.
Structure and Function[edit | edit source]
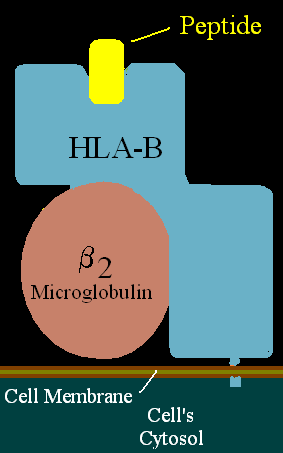
HLA-B7 is a class I major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecule. It is composed of a heavy chain (alpha chain) and a light chain (beta-2 microglobulin). The heavy chain is encoded by the HLA-B gene located on chromosome 6. The primary function of HLA-B7, like other class I MHC molecules, is to present endogenous peptides to cytotoxic T cells (CD8+ T cells). This process is crucial for the immune system to recognize and eliminate infected or malignant cells.
Genetics[edit | edit source]
The HLA-B7 serotype corresponds to the HLA-B*07 allele group. This group includes several alleles, such as HLA-B*0702, HLA-B*0703, and others. These alleles differ by a few amino acids in the peptide-binding region, which can influence the repertoire of peptides they present and their interaction with T cell receptors.
Disease Associations[edit | edit source]
HLA-B7 has been associated with various diseases, including:
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Psoriasis
- Reactive arthritis
- HIV progression
The presence of HLA-B7 can influence the susceptibility to these diseases and the course of the disease. For example, individuals with HLA-B7 may have a different progression rate of HIV infection compared to those without this allele.
Population Distribution[edit | edit source]
The frequency of HLA-B7 varies among different populations. It is relatively common in European populations and less frequent in Asian and African populations. The distribution of HLA-B7 and other HLA alleles is of interest in population genetics and anthropology.
Clinical Relevance[edit | edit source]
HLA typing, including HLA-B7, is important in several clinical contexts:
- Organ transplantation: Matching HLA alleles between donors and recipients can reduce the risk of transplant rejection.
- Bone marrow transplantation: HLA matching is critical for the success of bone marrow transplants.
- Disease risk assessment: Identifying HLA-B7 can help in assessing the risk for certain autoimmune diseases and infections.
See Also[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
External Links[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD