Myocardial bridge
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Myocardial bridge | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Often asymptomatic, angina, myocardial ischemia |
| Complications | Myocardial infarction, arrhythmia |
| Onset | |
| Duration | |
| Types | |
| Causes | Congenital |
| Risks | |
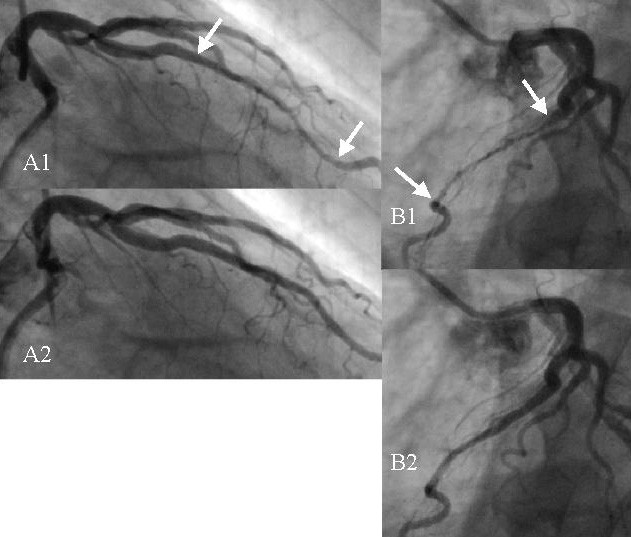
| Diagnosis | Coronary angiography, intravascular ultrasound |
| Differential diagnosis | |
| Prevention | |
| Treatment | Beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, surgery |
| Medication | |
| Prognosis | Generally good if asymptomatic |
| Frequency | 5-40% in the general population |
| Deaths | |
A congenital heart anomaly involving the coronary arteries
A myocardial bridge is a congenital anomaly of the coronary arteries where a segment of a coronary artery tunnels through the myocardium, the muscular wall of the heart, instead of resting on its surface. This condition is most commonly found in the left anterior descending artery (LAD), but can occur in other coronary arteries as well.
Anatomy and Physiology[edit | edit source]
In a typical heart, the coronary arteries lie on the surface of the heart, supplying oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle. In the case of a myocardial bridge, a portion of the artery dips into the myocardium and is "bridged" by heart muscle. During systole, when the heart muscle contracts, the tunneled segment of the artery is compressed, which can potentially reduce blood flow.
Clinical Significance[edit | edit source]
While many individuals with a myocardial bridge are asymptomatic, some may experience symptoms such as angina, myocardial ischemia, or even myocardial infarction. The compression of the artery during systole can lead to decreased blood flow, particularly during periods of increased heart rate or demand.
Symptoms[edit | edit source]
Symptoms associated with myocardial bridges can include:
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
Myocardial bridges are often diagnosed using imaging techniques such as:
Treatment[edit | edit source]
Treatment for myocardial bridges depends on the severity of symptoms. Options include:
- Beta-blockers or calcium channel blockers to reduce heart rate and myocardial contractility
- Surgical intervention, such as myotomy, in severe cases
- Lifestyle modifications to reduce cardiac stress
See also[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD

