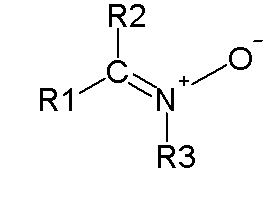
Nitrone
A nitrone is an organic compound with the general formula R1R2C=NO-R3, where R1 and R2 can be hydrogen, alkyl, or aryl groups, and R3 is an alkyl or aryl group. Nitrones are characterized by a carbon-nitrogen double bond (C=N) adjacent to an oxygen atom. They are a class of nitrogen-containing compounds that play a significant role in various chemical reactions, particularly in organic synthesis and medicinal chemistry.
Properties and Structure[edit | edit source]
Nitrones are known for their unique structure, which imparts stability and reactivity. The presence of the polar C=N-O moiety allows nitrones to participate in a range of chemical reactions, making them versatile intermediates in organic synthesis. The stability of nitrones is attributed to the resonance stabilization of the N-O group, which contributes to their relatively low reactivity compared to other nitrogen-oxygen compounds like nitroso compounds.
Synthesis[edit | edit source]
Nitrones are typically synthesized through the oxidation of N-alkylhydroxylamines or the condensation of aldehydes or ketones with hydroxylamine. The choice of synthesis method depends on the desired nitrone's structure and the starting materials available. The synthesis of nitrones is a crucial step in the preparation of various organic compounds, including spin traps used in electron spin resonance (ESR) spectroscopy.
Applications[edit | edit source]
- Spin Trapping###
One of the most notable applications of nitrones is in the field of spin trapping, a technique used in ESR spectroscopy to detect short-lived free radicals. Nitrones, due to their ability to react with free radicals forming stable adducts, are ideal for this purpose. This application is particularly important in the study of biological systems and the investigation of oxidative stress-related diseases.
- Organic Synthesis###
In organic synthesis, nitrones are used as precursors in the synthesis of amines, amides, and other nitrogen-containing compounds. They participate in various reactions, including cycloaddition reactions, such as the 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition, leading to the formation of isoxazolidines, which can be further manipulated to synthesize a wide range of organic compounds.
- Medicinal Chemistry###
In medicinal chemistry, nitrones have been explored for their potential therapeutic applications. Some nitrones, due to their ability to trap free radicals, are investigated for their neuroprotective properties and potential use in treating neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease.
Conclusion[edit | edit source]
Nitrones are a versatile class of organic compounds with significant applications in chemical research and potential therapeutic uses. Their unique structure and reactivity make them valuable intermediates in organic synthesis and important tools in the study of free radical chemistry.
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD