Carbohydrate
(Redirected from Saccharides)
Carbohydrates are a group of macromolecules that are vital for energy production, biological functions, and structural integrity in living organisms. They are one of the four major classes of biomolecules, alongside proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. Carbohydrates are composed of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen:oxygen atom ratio of 2:1, as in water, which gives these compounds their name (hydrates of carbon).
Types of Carbohydrates[edit | edit source]
Carbohydrates are classified into three main types based on their chemical structure and complexity: monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides.
Monosaccharides[edit | edit source]
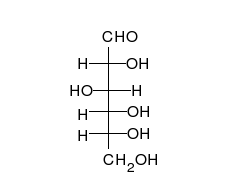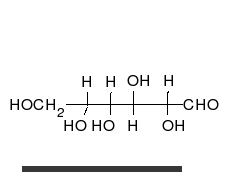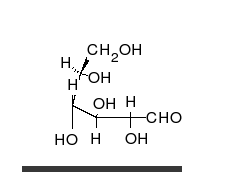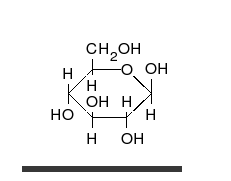
Monosaccharides are the simplest form of carbohydrates and cannot be hydrolyzed into simpler sugars. They are the building blocks of more complex carbohydrates. Common examples include glucose, fructose, and galactose. These sugars are involved in primary energy sources for metabolism and are critical in various biological processes.
Disaccharides[edit | edit source]
Disaccharides are formed when two monosaccharides undergo a dehydration reaction. Common examples include sucrose (table sugar), which is glucose + fructose, lactose (milk sugar), which is glucose + galactose, and maltose, which is two glucose molecules. Disaccharides are important in diet and nutrition, providing energy and sweetness to foods.
Polysaccharides[edit | edit source]
Polysaccharides are complex carbohydrates, consisting of long chains of monosaccharide units. They serve various functions such as energy storage (e.g., starch in plants and glycogen in animals) and structural support (e.g., cellulose in plants and chitin in the exoskeletons of insects and crustaceans). Polysaccharides are crucial for life, providing energy reserves and structural integrity to cells and tissues.
Functions of Carbohydrates[edit | edit source]
Carbohydrates play several critical roles in living organisms, including:
- Energy Production: The primary role of carbohydrates is to provide energy for the body, especially through glucose, a monosaccharide that is a key energy source for cellular respiration.
- Structural Components: Carbohydrates like cellulose and chitin provide structural support to plants and animals, respectively.
- Cellular Communication: Certain carbohydrates on the cell surface are involved in cell-cell recognition and signaling.
- Energy Storage: Polysaccharides like starch and glycogen serve as energy storage molecules in plants and animals.
Dietary Importance[edit | edit source]
Carbohydrates are a crucial part of a healthy diet, providing the body with glucose for energy. Dietary guidelines recommend that carbohydrates make up about 45% to 65% of total daily calories. However, the type of carbohydrates consumed is important; complex carbohydrates and dietary fibers are preferred over simple sugars for better health outcomes.
Metabolism[edit | edit source]
Carbohydrate metabolism involves various biochemical processes that are crucial for generating energy. The most well-known pathway is glycolysis, where glucose is broken down to produce ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the energy currency of the cell. Other important pathways include the Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation, which further process the products of glycolysis to produce ATP.
This article is a biochemistry stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD