CHARGE syndrome
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| CHARGE syndrome | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | |
| Pronounce | |
| Specialty | Medical genetics |
| Symptoms | Coloboma, heart defects, atresia of the choanae, growth retardation, genital abnormalities, ear abnormalities |
| Complications | N/A |
| Onset | |
| Duration | |
| Types | |
| Causes | Genetic mutation |
| Risks | |
| Diagnosis | Clinical diagnosis, genetic testing |
| Differential diagnosis | |
| Prevention | |
| Treatment | Supportive care, surgery |
| Medication | |
| Prognosis | |
| Frequency | 1 in 8,500 to 10,000 births |
| Deaths | |
CHARGE Syndrome: An In-depth Look[edit | edit source]
CHARGE syndrome is a congenital disorder that manifests in multiple bodily regions right from birth. The name CHARGE is an acronym detailing the core manifestations of the syndrome:
- C - Coloboma: A defect in the eye structure
- H - Heart defect: Cardiac anomalies
- A - Atresia Choanae: Often referred to as choanal atresia, this pertains to blockages in the nasal passages
- R - Restricted growth and development: Developmental delays and growth impediments
- G - Genital abnormality: Defects in the reproductive organs
- E - Ear abnormality: Structural and functional ear anomalies
Synonyms[edit | edit source]
- Coloboma, heart anomaly, choanal atresia, retardation, genital and ear anomalies
- CHARGE association
- Hall-Hittner syndrome
Clinical Presentation[edit | edit source]
While the aforementioned symptoms form the crux of CHARGE syndrome, not every individual with the disorder will exhibit all these features. The presentation can be diverse, with some showing mild symptoms and others experiencing severe complications.
Eye and Vision[edit | edit source]
Coloboma represents a gap or defect in one of the eye's structures, often in the retina or iris. It may lead to vision impairment or, in certain cases, blindness.
Heart Anomalies[edit | edit source]
Heart defects can range from minor anomalies, which might not require any intervention, to more severe forms that necessitate surgical procedures.
Nasal Passages and Breathing[edit | edit source]
Choanal atresia can make breathing arduous, particularly in newborns, as they predominantly breathe through their noses. Surgical intervention may be required to clear the blockages.
Growth and Development[edit | edit source]
Individuals with CHARGE syndrome may showcase delays in reaching developmental milestones. This could encompass speech delays, mobility challenges, or cognitive impairments.
Reproductive Organs[edit | edit source]
Genital abnormalities can lead to fertility issues in the future and might also affect physical development during puberty.
Hearing and Balance[edit | edit source]
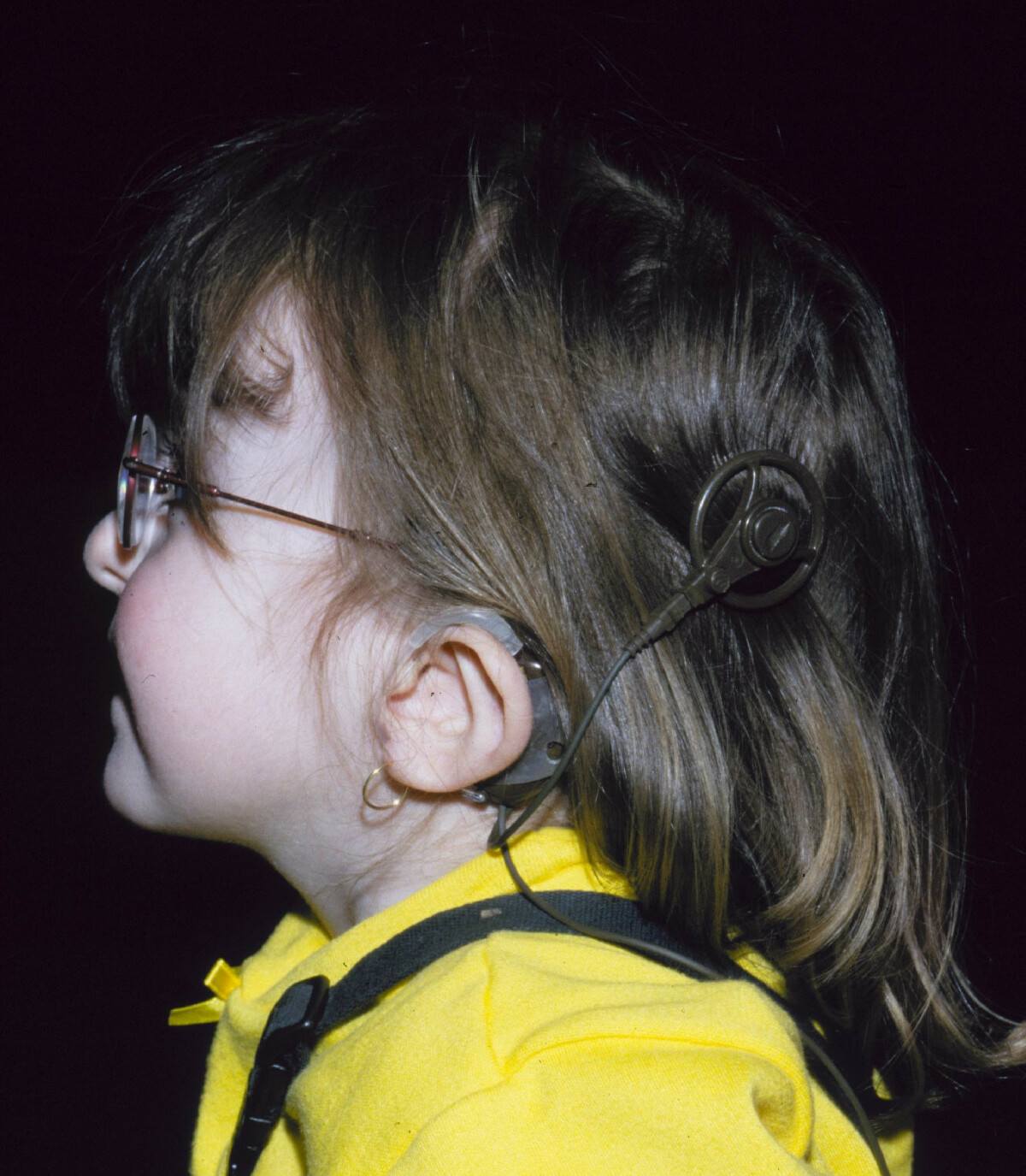
Ear abnormalities can result in hearing loss or balance-related issues. Regular assessments and interventions, such as hearing aids, can help address these challenges.
Epidemiology[edit | edit source]
CHARGE syndrome occurs in approximately 1 in 8,500 to 10,000 newborns.
Cause[edit | edit source]
Mutations in the CHD7 gene cause most cases of CHARGE syndrome. The CHD7 gene provides instructions for making a protein that regulates gene activity (expression) by a process known as chromatin remodeling. Chromatin is the complex of DNA and protein that packages DNA into chromosomes. The structure of chromatin can be changed (remodeled) to alter how tightly DNA is packaged. When DNA is tightly packed, gene expression is lower than when DNA is loosely packed. Chromatin remodeling is one way gene expression is regulated during development. Most mutations in the CHD7 gene lead to the production of an abnormal CHD7 protein that is broken down prematurely. Shortage of this protein is thought to disrupt chromatin remodeling and the regulation of gene expression. Changes in gene expression during embryonic development likely cause the signs and symptoms of CHARGE syndrome. A small percentage of individuals with CHARGE syndrome do not have an identified mutation in the CHD7 gene. Some of them may have a genetic change affecting the CHD7 gene that has not been found, and others may have a change in a different gene, although additional genes associated with CHARGE syndrome have not been identified.
Inheritance[edit | edit source]
When CHARGE syndrome is caused by mutations in the CHD7 gene, it follows an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance, which means one copy of the altered gene in each cell is sufficient to cause the disorder. Most cases result from new mutations in the gene and occur in people with no history of the disorder in their family. In rare cases, an affected person inherits the mutation from an affected parent. The inheritance pattern of other cases of CHARGE syndrome is unknown.
Signs and symptoms[edit | edit source]
Affected individuals usually have several major characteristics or a combination of major and minor characteristics. The major characteristics of CHARGE syndrome are common in this disorder and occur less frequently in other disorders.
- Most individuals with CHARGE syndrome have a gap or hole in one of the structures of the eye (coloboma), which forms during early development. A coloboma may be present in one or both eyes and may impair a person's vision, depending on its size and location.
- Some affected individuals also have abnormally small or underdeveloped eyes (microphthalmia).
- In many people with CHARGE syndrome, one or both nasal passages are narrowed (choanal stenosis) or completely blocked (choanal atresia), which can cause difficulty breathing.
- Affected individuals frequently have cranial nerve abnormalities. The cranial nerves emerge directly from the brain and extend to various areas of the head and neck, controlling muscle movement and transmitting sensory information.
- Abnormal function of certain cranial nerves can cause swallowing problems, facial paralysis, a sense of smell that is diminished (hyposmia) or completely absent (anosmia), and mild to profound hearing loss. People with CHARGE syndrome also typically have middle and inner ear abnormalities, which can contribute to hearing problems, and unusually shaped external ears.
While the minor characteristics of CHARGE syndrome are common in this disorder, they are also frequently present in people without the disorder.
- The minor characteristics include heart defects; slow growth starting in late infancy; delayed development of motor skills, such as sitting unsupported and walking; and an opening in the lip (cleft lip) with or without an opening in the roof of the mouth (cleft palate).
- Affected individuals frequently have hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, which affects the production of hormones that direct sexual development. As a result, males with CHARGE syndrome are often born with an unusually small penis (micropenis) and undescended testes (cryptorchidism).
- Abnormalities of external genitalia are seen less often in affected females. Puberty can be incomplete or delayed in affected males and females.
- Another minor feature of CHARGE syndrome is tracheoesophageal fistula, which is an abnormal connection (fistula) between the esophagus and the trachea.
- Most people with CHARGE syndrome also have distinctive facial features, including a square-shaped face and differences in appearance between the right and left sides of the face (facial asymmetry). Affected individuals have a wide range of cognitive function, from normal intelligence to major learning disabilities with absent speech and poor communication.
Less common features of CHARGE syndrome include kidney abnormalities; immune system problems; abnormal curvature of the spine (scoliosis or kyphosis); and limb abnormalities, such as extra fingers or toes (polydactyly), missing fingers or toes (oligodactyly), an inward and upward turning foot (club foot), and abnormalities of the long bones of the arms and legs.
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
Genetic testing is available for CHARGE syndrome. The CHD7 gene is the only gene in which mutations are known to cause CHARGE syndrome. The CHD7 mutation detection rate when sequence analysis is performed is estimated to be 65%-70% for all typical and suspected cases combined.
Treatment[edit | edit source]
Management of the manifestations of CHD7 disorder can be complex and require a multidisciplinary approach involving clinicians, therapists, and educators.
Diagnosis and Treatment[edit | edit source]
Diagnosis of CHARGE syndrome primarily hinges on clinical evaluation and detailed patient history. Genetic testing can further affirm the diagnosis by pinpointing mutations in the CHD7 gene, commonly associated with this syndrome. Treatment is largely symptomatic and supportive, with specialists addressing each symptom in a targeted manner. Regular monitoring and early intervention can vastly improve the quality of life for individuals with CHARGE syndrome.
Conclusion[edit | edit source]
CHARGE syndrome, though rare, presents a spectrum of challenges that require a multidisciplinary approach for management. Early diagnosis and tailored interventions are pivotal in ensuring optimal outcomes for affected individuals.
| Disorders of transcription and post transcriptional modification | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Congenital abnormality syndromes (Q87, 759.7) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
NIH genetic and rare disease info[edit source]
CHARGE syndrome is a rare disease.
| Rare and genetic diseases | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Rare diseases - CHARGE syndrome
|
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Kondreddy Naveen, Prab R. Tumpati, MD


