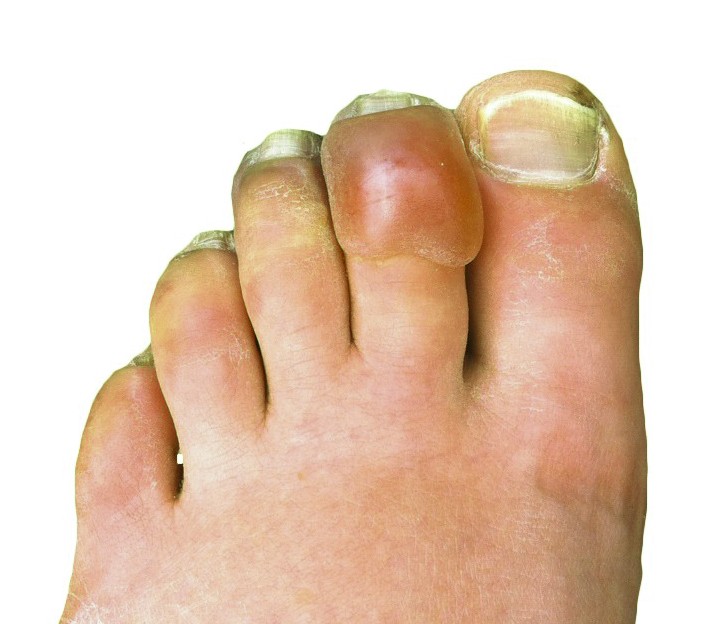
Frostbite
(Redirected from Cold burn)
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Frostbite | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Cold skin, numbness, clumsiness, blistering after rewarming |
| Complications | Gangrene, infection, hypothermia |
| Onset | Gradual with exposure to cold |
| Duration | Varies, can be permanent |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Exposure to extreme cold |
| Risks | Alcohol consumption, smoking, diabetes, peripheral neuropathy |
| Diagnosis | Based on symptoms and physical examination |
| Differential diagnosis | Chilblains, trench foot, Raynaud's phenomenon |
| Prevention | Proper clothing, avoiding prolonged exposure to cold |
| Treatment | Rewarming, pain management, wound care, possible surgery |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Depends on severity; possible permanent damage |
| Frequency | Common in cold climates |
| Deaths | Rare, but possible due to complications |
| Frostbite | |
|---|---|
|
|
|
| ICD-10 | T33
-T35 |
| ICD-9 | 991.0-991.3 |
| DiseasesDB | 31167 |
| MedlinePlus | 000057 |
| eMedicine | emerg 209 med/2815
derm/833 ped/803 |
| MeSH ID | D00562 |
Over-the-counter (OTC) drugs are a class of medications that can be purchased without the requirement of a doctor's prescription. They are primarily used for the treatment of common, non-serious, and self-diagnosable health conditions.
Classification and Examples[edit | edit source]
These drugs encompass a broad spectrum of classes and offer a range of remedies for conditions such as pain, cold, allergies, constipation, and heartburn. Examples include analgesics like aspirin and acetaminophen, antihistamines, and antacids. OTC drugs also cover dietary supplements, vitamins, and skincare products, among others.
Regulations[edit | edit source]
The availability of OTC drugs is regulated by the country's drug regulatory authority, like the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States. These agencies classify drugs based on their safety profile, potential for misuse, and necessity for a physician's supervision during treatment.
Safety and Risks[edit | edit source]
While OTC drugs are generally safe for public consumption, misuse or overuse can lead to adverse effects or drug interactions. As such, reading and understanding the label instructions and warnings is crucial. Certain groups, such as pregnant women, children, and older adults, may be more susceptible to the risks associated with OTC drugs and should exercise caution.
Role in Healthcare[edit | edit source]
OTC drugs play an essential role in healthcare, offering convenient, cost-effective, and immediate access to medications for minor health issues. They reduce the burden on healthcare professionals and facilities by enabling self-care and preventive care.
Frostbite gallery[edit | edit source]
See Also[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- "Over-the-counter (OTC) drugs." U.S. Food and Drug Administration. [1]
- "The benefits and risks of over-the-counter medications." Johns Hopkins Medicine. [2]
References[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD









