Conjunctival squamous cell carcinoma
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Conjunctival squamous cell carcinoma | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Red eye, eye irritation, vision loss |
| Complications | Metastasis, vision impairment |
| Onset | Typically in adulthood |
| Duration | Chronic |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Human papillomavirus, ultraviolet light exposure |
| Risks | Immunosuppression, HIV/AIDS, xeroderma pigmentosum |
| Diagnosis | Biopsy, slit lamp examination |
| Differential diagnosis | Pinguecula, pterygium, conjunctivitis |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Surgical excision, cryotherapy, topical chemotherapy |
| Medication | Mitomycin C, 5-fluorouracil |
| Prognosis | Generally good with treatment |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |
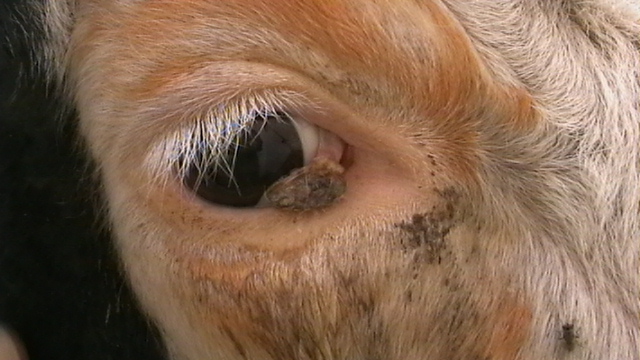
Conjunctival Squamous Cell Carcinoma (CSCC) is a type of cancer that occurs on the conjunctiva, which is the thin, transparent membrane covering the white part of the eye and the inner surfaces of the eyelids. CSCC is a form of squamous cell carcinoma, which is characterized by the abnormal growth of squamous cells. While it is a rare condition, it is considered the most common malignancy of the ocular surface.
Causes and Risk Factors[edit | edit source]
The exact cause of CSCC is not fully understood, but several risk factors have been identified. Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation is considered a significant risk factor, as it can cause damage to the DNA of conjunctival cells. Other risk factors include exposure to certain chemicals (such as arsenic), Human Papillomavirus (HPV) infection, and immunosuppressive conditions.
Symptoms[edit | edit source]
Symptoms of CSCC may include a noticeable growth on the conjunctiva, redness or irritation of the eye, a sensation of a foreign body in the eye, and in some cases, vision impairment. The appearance of the tumor can vary, but it often presents as a pink, fleshy mass. It is important to note that early stages of CSCC may be asymptomatic.
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
Diagnosis of CSCC involves a thorough examination of the eye by an ophthalmologist. This may include slit-lamp examination, biopsy of the lesion, and imaging tests such as ultrasound or MRI to determine the extent of the tumor. Histopathological examination of the biopsy sample is crucial for confirming the diagnosis.
Treatment[edit | edit source]
Treatment options for CSCC depend on the size, location, and extent of the tumor, as well as the overall health of the patient. Small, localized tumors may be treated with surgical excision, while larger or more aggressive tumors may require additional therapies such as cryotherapy, radiotherapy, or chemotherapy. In some cases, a combination of treatments may be necessary. Early detection and treatment are key to preventing the spread of the cancer and preserving vision.
Prognosis[edit | edit source]
The prognosis for patients with CSCC is generally good, especially when the cancer is detected and treated early. However, the risk of recurrence is significant, and regular follow-up with an ophthalmologist is important for early detection of any recurrence or new tumors.
Prevention[edit | edit source]
Preventive measures against CSCC include protecting the eyes from excessive UV exposure by wearing UV-protective sunglasses and hats when outdoors. Regular eye examinations are also important, particularly for individuals at higher risk due to known risk factors.
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD

