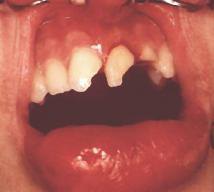
Dental traumatology
Dental Traumatology[edit | edit source]
Dental traumatology deals with injuries to the teeth and their supporting structures. This branch of dentistry encompasses various types of trauma affecting the teeth, gums, periodontal ligament, alveolar bone, and nearby soft tissues such as the lips and tongue. Understanding dental trauma is crucial for effective treatment and prevention of further complications.
Types of Dental Injuries[edit | edit source]
Dental trauma can affect different parts of the mouth and manifest in various forms, including:
Dental Injuries[edit | edit source]
- Enamel Infraction: Minor damage to the tooth enamel without loss of tooth structure.
- Enamel Fracture: A crack or break in the tooth's enamel layer.
- Enamel-Dentine Fracture: A fracture affecting both the enamel and the underlying dentine layer.
- Enamel-Dentine Fracture Involving Pulp: A more severe fracture that exposes the tooth's pulp.
- Root Fracture: A break in the root portion of the tooth.
Periodontal Injuries[edit | edit source]
- Concussion: Injury causing tooth sensitivity but not displacement.
- Subluxation: A tooth knocked loose without being displaced.
- Luxation: The tooth is displaced from its original position, including extrusive, intrusive, and lateral movements.
- Avulsion: Complete displacement of the tooth from its socket.
Injuries to Supporting Bone[edit | edit source]
Injuries involving the alveolar bone can range from minor fractures to significant disruptions affecting the stability of teeth. Types of bone injuries include comminuted fractures, fractures of the socket wall, dentoalveolar fractures, and fractures extending to the maxilla or mandible.
Signs and Symptoms[edit | edit source]
Recognizing dental trauma involves noticing changes in occlusion, movement of multiple teeth as a single segment, bruising of the gums, and potential lacerations across the fracture line.
Treatment Approaches[edit | edit source]
The treatment for dental trauma varies based on the type and severity of the injury. It may involve repositioning and stabilizing displaced teeth, splinting loose teeth, and suturing soft tissue lacerations. In cases of avulsion, immediate action is critical to attempt re-implantation of the tooth.
Soft Tissue Laceration[edit | edit source]
Soft tissue injuries, including those to the lips, buccal mucosa, and tongue, require careful examination to rule out foreign objects and assess for potential complications like damage to the facial nerve or parotid duct.
Primary Teeth Trauma[edit | edit source]
In young children, trauma to primary teeth is common and treatment prioritizes the health and development of the underlying permanent teeth. Strategies include removing displaced primary teeth that risk damaging the permanent tooth germ.
Permanent Teeth Trauma[edit | edit source]
For permanent teeth, treatments aim to preserve the tooth structure and pulp vitality when possible, through methods like pulp capping, partial pulpotomy, or root canal treatment, depending on the extent of pulp exposure.
Glossary[edit | edit source]
- Occlusion (dentistry)|Occlusion: The contact between teeth.
- Periodontal Ligament: The tissue that helps anchor teeth to the jawbone.
- Alveolar Bone: The part of the jawbone that holds the tooth sockets.
- Soft Tissue: Tissues surrounding and supporting the teeth, including gums and mucosa.
| Dental traumatology Resources | |
|---|---|
|
|
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD