Hair loss
(Redirected from Diffuse alopecia)
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Hair loss | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Alopecia, baldness |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | Dermatology |
| Symptoms | Loss of hair from part of the head or body |
| Complications | Psychological stress, social anxiety |
| Onset | Can begin at any age |
| Duration | Can be temporary or permanent |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Genetics, hormonal changes, medical conditions, medications |
| Risks | Family history, age, significant weight loss, certain medical conditions |
| Diagnosis | Physical examination, medical history, scalp biopsy |
| Differential diagnosis | Telogen effluvium, trichotillomania, tinea capitis |
| Prevention | Avoiding tight hairstyles, balanced diet, managing stress |
| Treatment | Medications, hair transplant, laser therapy |
| Medication | Minoxidil, finasteride |
| Prognosis | N/A |
| Frequency | Common, affects millions worldwide |
| Deaths | N/A |

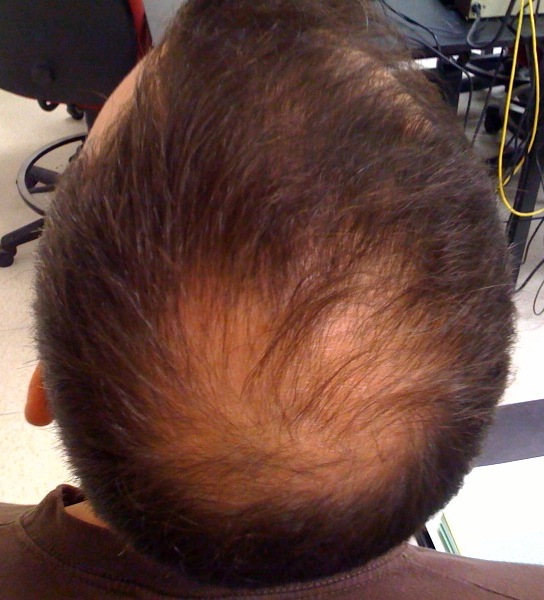
Hair loss, also known as baldness, is a condition in which an individual lacks hair in areas where it typically grows, particularly on the scalp. The most prevalent form of hair loss is androgenic alopecia, commonly referred to as male pattern baldness. This progressive hair thinning condition affects adult human males and some primate species. However, hair loss can take various forms and manifest with differing severity, from male and female pattern alopecia (androgenetic alopecia), alopecia areata, alopecia totalis, to the most extreme form, alopecia universalis. Treatment for hair loss has limited success; the greater the amount of hair lost, the less effective the treatment is likely to be.
Causes and Types of Hair Loss[edit | edit source]
- Pattern baldness - The incidence of pattern baldness varies among populations, influenced by factors such as diet and personal habits. Male pattern baldness is characterized by hair receding from the lateral sides of the forehead and the possible development of an additional bald patch on top. This type of baldness, androgenic alopecia, is triggered by dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a potent sex hormone. Female pattern baldness is less common and typically results from a decrease in estrogen, which counteracts the balding effect of testosterone.
- Traction alopecia - Commonly found in individuals with ponytails or cornrows who apply excessive force to their hair. Wearing a hat is not generally a cause, but it is advisable to let the scalp breathe for at least 7 hours a day.
- Telogen effluvium - Traumas such as chemotherapy, childbirth, major surgery, poisoning, and severe stress can cause this hair loss condition.
- Fungal infections - Some mycotic infections can lead to massive hair loss.
- Alopecia areata - An autoimmune disorder, also known as "spot baldness," which can result in hair loss ranging from a single location to the entire body.
- Cicatricial alopecia - Localized or diffuse hair loss may occur in cases of cicatricial alopecia, which is related to conditions like lupus erythematosus, lichen plano pilaris, folliculitis decalvans, central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia, and postmenopausal frontal fibrosing alopecia.
- Hypothyroidism - This condition can cause hair loss, especially thinning of the outer third of the eyebrows.
Etymology[edit | edit source]
The term "alopecia" comes from the Greek word "alopex," meaning fox, as foxes shed their coats twice a year. The term "bald" is derived from the English word "balde," which means "white."
Treatments for Hair Loss[edit | edit source]
A variety of treatments are available to help manage hair loss. Effectiveness varies depending on the individual, the type of hair loss, and the severity of the condition. Some common treatments include:
- Minoxidil (Rogaine): An FDA-approved topical treatment for hair loss. It is a vasodilator that increases blood flow to the hair follicles, promoting hair growth. It works best in the early stages of hair loss.
- Finasteride (Propecia): A prescription medication that inhibits the production of DHT, thus slowing down the progression of male pattern baldness. It is not approved for use in women.
- Dutasteride (Avodart): Similar to finasteride, it blocks the production of DHT but is more potent. It is not approved by the FDA for treating hair loss but has been used off-label.
- Spironolactone (Aldactone): A diuretic drug that has anti-androgenic effects and is sometimes used off-label to treat female pattern baldness.
- Corticosteroids: Used to treat alopecia areata, these can be injected directly into the affected areas or taken orally.
- Anthralin (Dritho-Scalp): A topical medication used to treat psoriasis that may also stimulate hair growth in people with alopecia areata.
- Hair Transplant Surgery: A surgical procedure that involves removing hair follicles from a part of the scalp with healthy hair growth and transplanting them to areas with thinning hair or baldness.
- Scalp Micropigmentation: A cosmetic tattooing procedure that creates the appearance of hair stubble or a fuller head of hair by injecting pigment into the scalp.
- Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT): A non-invasive treatment that uses red light or near-infrared light to stimulate hair growth. The effectiveness of LLLT for hair loss is still debated.
Coping with Hair Loss[edit | edit source]
The psychological implications of hair loss can significantly impact an individual's self-confidence, with the most severe effects typically occurring at the onset of symptoms. However, some people embrace their baldness, drawing inspiration from charismatic bald celebrities, politicians, or sportsmen who are considered masculine and attractive. Various companies have built successful businesses selling hair loss reversal products, such as hair regrowth treatments, hair transplants, and hairpieces.
Preventing and Reversing Hair Loss[edit | edit source]
Preventing healthy hairs from falling out is easier than regrowing hair in dormant follicles. Finasteride (Propecia) and minoxidil (Rogaine) have shown some success in partially reversing hair loss, although they are generally ineffective in treating extreme cases. Hair multiplication or hair cloning, a treatment under development, shows promise in mice and could become available to the public in the near future.
| This article is a medical stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it! | |
|---|---|
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD




