Foramen ovale (heart)
== Foramen ovale (heart) ==
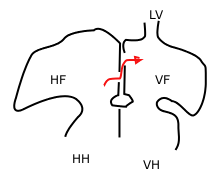
The foramen ovale is an important anatomical feature in the fetal circulation system. It is an opening in the septum between the right atrium and the left atrium of the heart. This opening allows blood to bypass the non-functioning fetal lungs and flow directly from the right atrium to the left atrium.
Development[edit | edit source]
The foramen ovale forms during the development of the fetal heart. It is a crucial component of the fetal circulation system, which includes the ductus arteriosus and the ductus venosus. These structures work together to ensure that oxygenated blood from the placenta is efficiently distributed throughout the fetus.
Function[edit | edit source]
In the fetus, the foramen ovale allows oxygen-rich blood from the umbilical vein to pass from the right atrium to the left atrium. This blood then enters the left ventricle and is pumped into the aorta, supplying the body with oxygenated blood. This bypass of the lungs is necessary because the fetal lungs are not yet functional and are filled with fluid.
Closure[edit | edit source]
After birth, the foramen ovale typically closes as the newborn begins to breathe and the pulmonary circulation becomes functional. The increased pressure in the left atrium, due to the influx of blood from the lungs, forces the foramen ovale to close. In most individuals, this closure is permanent, and the foramen ovale becomes the fossa ovalis.
Patent Foramen Ovale[edit | edit source]
In some individuals, the foramen ovale does not close completely after birth, resulting in a condition known as patent foramen ovale (PFO). A PFO can allow blood to flow between the atria, which may lead to various health issues, including an increased risk of stroke and migraines.
Clinical Significance[edit | edit source]
The presence of a patent foramen ovale can be detected using diagnostic tools such as echocardiography. Treatment options for PFO may include medical management or surgical intervention, depending on the severity of the condition and the presence of symptoms.
See Also[edit | edit source]
| Congenital heart diseases | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
This congenital heart disease related article is a stub.
|
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD