Gastric bypass surgery
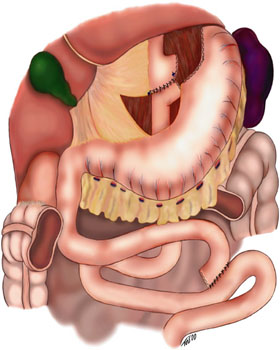
Gastric bypass surgery is a type of bariatric surgery that involves creating a small pouch from the stomach and connecting the newly created pouch directly to the small intestine. This procedure is used to treat morbid obesity and related conditions such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and sleep apnea.
Types of Gastric Bypass Surgery[edit | edit source]
There are several types of gastric bypass surgery, including:
- Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB): This is the most common type of gastric bypass surgery. It involves creating a small pouch at the top of the stomach and connecting it directly to the small intestine, bypassing a large part of the stomach and the first section of the small intestine (duodenum).
- Mini-Gastric Bypass (MGB): This is a simpler and shorter procedure compared to RYGB. It involves creating a long, narrow tube of the stomach and attaching it to the small intestine.
Procedure[edit | edit source]
The procedure is typically performed using laparoscopic surgery, which involves making small incisions and using a camera to guide the surgery. The surgeon creates a small stomach pouch and then connects it to the small intestine, bypassing the rest of the stomach and the upper part of the small intestine.
Benefits[edit | edit source]
Gastric bypass surgery can lead to significant weight loss and improvement in obesity-related conditions. Benefits include:
- Significant and sustained weight loss
- Improvement or resolution of type 2 diabetes
- Reduction in hypertension
- Improvement in sleep apnea
- Enhanced quality of life
Risks and Complications[edit | edit source]
As with any major surgery, gastric bypass surgery carries risks and potential complications, including:
Postoperative Care[edit | edit source]
After the surgery, patients need to follow a strict diet and lifestyle changes to ensure successful weight loss and avoid complications. This includes:
- Eating small, frequent meals
- Avoiding high-sugar and high-fat foods
- Taking vitamin and mineral supplements
- Regular follow-up with healthcare providers
See Also[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
External Links[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD