Giardiasis
(Redirected from Lambliasis)
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Giardiasis | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Diarrhea, abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, fatigue |
| Complications | Malabsorption, dehydration |
| Onset | 1 to 3 weeks after exposure |
| Duration | 2 to 6 weeks |
| Types | N/A |
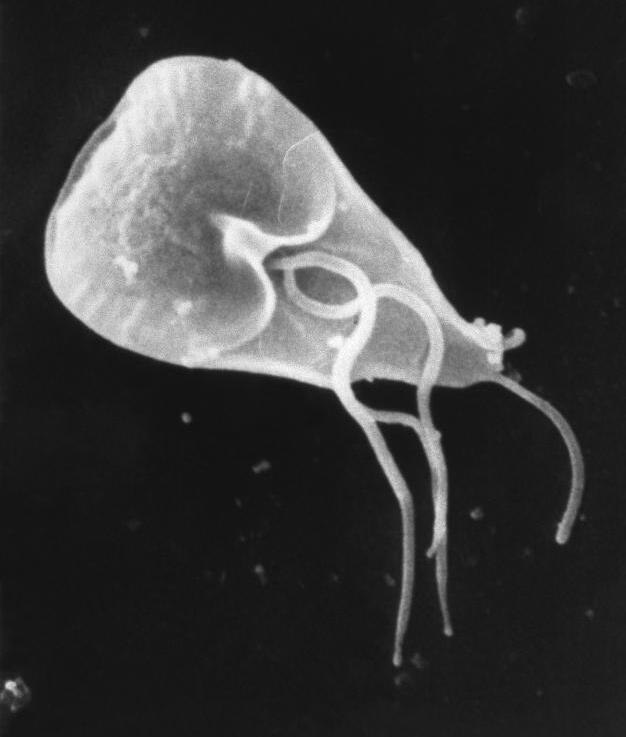
| Causes | Giardia lamblia |
| Risks | Contaminated water, poor sanitation, travel to endemic areas |
| Diagnosis | Stool test, antigen test, PCR |
| Differential diagnosis | Irritable bowel syndrome, lactose intolerance, Crohn's disease |
| Prevention | Boiling water, water filtration, handwashing |
| Treatment | Metronidazole, tinidazole, nitazoxanide |
| Medication | Antibiotics |
| Prognosis | N/A |
| Frequency | Common in developing countries |
| Deaths | Rare |
Giardiasis is a common intestinal infection caused by the microscopic parasite Giardia lamblia. It is one of the most common causes of waterborne disease worldwide and can affect both humans and animals. Giardiasis is prevalent in areas with poor sanitation or contaminated water sources.
Transmission and Lifecycle[edit | edit source]
Giardiasis is typically transmitted through the ingestion of water or food contaminated with Giardia cysts, the hardy form of the parasite. The cysts can survive in the environment, including in water sources, for extended periods. Once ingested, the cysts release trophozoites, the active form of the parasite, in the small intestine. The trophozoites attach to the intestinal lining and multiply, leading to symptoms and the potential for transmission to others.
Symptoms[edit | edit source]
- Not all individuals infected with Giardia lamblia will develop symptoms, but common signs and symptoms of giardiasis can include:
- Diarrhea: Diarrhea is the most common symptom, often watery and foul-smelling, which may alternate with periods of normal or loose stools.
- Abdominal Pain: Abdominal cramps and discomfort, often centered around the upper abdomen, may occur.
- Bloating and Gas: Increased flatulence and bloating may be experienced.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Some individuals may experience nausea and vomiting, although this is less common.
- Weight Loss: Prolonged giardiasis can lead to weight loss and malabsorption of nutrients.
- Symptoms typically appear within 1 to 3 weeks after exposure and can last for several weeks or longer if left untreated.
Diagnosis and Treatment[edit | edit source]
- To diagnose giardiasis, a stool sample is typically analyzed for the presence of Giardia cysts or trophozoites. In some cases, multiple stool samples may be required to increase the likelihood of detection.
- Treatment for giardiasis involves the use of specific antiparasitic medications, such as metronidazole or tinidazole. These medications are effective in eliminating the parasite and relieving symptoms. It is important to complete the full course of treatment as prescribed by a healthcare professional.
Prevention[edit | edit source]
- Preventing giardiasis involves taking measures to minimize the risk of exposure to the parasite:
- Safe Water Practices: Drink and use water from safe, treated sources. If the water source is uncertain, boiling or filtering the water can help reduce the risk of infection.
- Good Hygiene: Practice proper hand hygiene, especially before eating and after using the restroom, to minimize the risk of fecal-oral transmission.
- Food Safety: Ensure proper food handling and preparation to prevent contamination.
- Avoiding Swallowing Contaminated Water: Take precautions while swimming in lakes, rivers, or pools, and avoid swallowing water that may be contaminated.
Summary[edit | edit source]
Giardiasis is a common intestinal infection caused by the parasite Giardia lamblia. It is typically transmitted through contaminated water or food sources. Prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment with antiparasitic medications can effectively eliminate the parasite and relieve symptoms. Preventive measures, such as safe water practices and good hygiene, are essential in minimizing the risk of giardiasis.
See Also[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD


