Robinow syndrome
(Redirected from Mesomelic dwarfism-small genitalia syndrome)
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Robinow syndrome | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Fetal face syndrome |
| Pronounce | |
| Specialty | Medical genetics |
| Symptoms | Short stature, limb shortening, genital hypoplasia, craniofacial dysmorphism |
| Complications | N/A |
| Onset | Birth |
| Duration | Lifelong |
| Types | Autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive |
| Causes | Genetic mutations in ROR2 or WNT5A genes |
| Risks | Family history |
| Diagnosis | Clinical evaluation, genetic testing |
| Differential diagnosis | Achondroplasia, Ellis-van Creveld syndrome |
| Prevention | Genetic counseling |
| Treatment | Symptomatic management, orthopedic surgery, hormone therapy |
| Medication | |
| Prognosis | Variable, generally normal life expectancy |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | |
Robinow syndrome is a rare genetic disorder characterized by distinctive facial features, limb shortening, and genital abnormalities. It was first described by the German geneticist Meinhard Robinow in 1969. The syndrome can be inherited in an autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive manner.
Clinical Features[edit | edit source]
Individuals with Robinow syndrome typically present with:
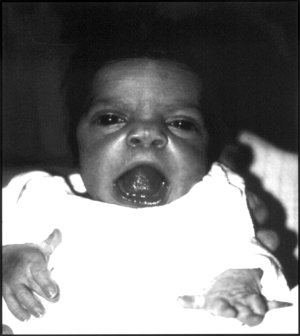
- Facial dysmorphism: This includes a broad forehead, hypertelorism (wide-set eyes), a short nose with an upturned tip, and a wide mouth.
- Limb shortening: Shortening of the arms and legs, particularly the forearms and lower legs.
- Genital abnormalities: Males may have micropenis and undescended testes, while females may have underdeveloped genitalia.
- Vertebral anomalies: Abnormalities in the spine, such as hemivertebrae or scoliosis.
- Growth retardation: Short stature is common in individuals with Robinow syndrome.
Genetics[edit | edit source]
Robinow syndrome can be caused by mutations in several genes, including ROR2 and WNT5A. The autosomal dominant form is often associated with mutations in the WNT5A gene, while the autosomal recessive form is typically linked to mutations in the ROR2 gene.
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
The diagnosis of Robinow syndrome is primarily based on clinical features and can be confirmed through genetic testing. Prenatal diagnosis is possible if there is a known family history of the disorder.
Management[edit | edit source]
There is no cure for Robinow syndrome, and treatment is symptomatic and supportive. Management may include:
- Orthopedic surgery: To address limb and spine abnormalities.
- Hormone therapy: For genital abnormalities.
- Physical therapy: To improve mobility and muscle strength.
- Genetic counseling: For affected families to understand the inheritance pattern and risks for future pregnancies.
Epidemiology[edit | edit source]
Robinow syndrome is extremely rare, with an estimated prevalence of less than 1 in 500,000 individuals. It affects both males and females equally.
See Also[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
External Links[edit | edit source]
-
See also[edit | edit source]
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP1 injections from $125
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program NYC and a clinic to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our W8MD's physician supervised medical weight loss centers in NYC provides expert medical guidance, and offers telemedicine options for convenience.
Why choose W8MD?
- Comprehensive care with FDA-approved weight loss medications including:
- loss injections in NYC both generic and brand names:
- weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion etc.
- Accept most insurances for visits or discounted self pay cost.
- Generic weight loss injections starting from just $125.00 for the starting dose
- In person weight loss NYC and telemedicine medical weight loss options in New York city available
- Budget GLP1 weight loss injections in NYC starting from $125.00 biweekly with insurance!
Book Your Appointment
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss, and Philadelphia medical weight loss Call (718)946-5500 for NY and 215 676 2334 for PA
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's NYC physician weight loss.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available. Call 718 946 5500.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD



