Nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma
(Redirected from NLPHL)
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Lymphadenopathy, fever, night sweats, weight loss |
| Complications | Transformation to diffuse large B-cell lymphoma |
| Onset | |
| Duration | |
| Types | |
| Causes | Unknown |
| Risks | |
| Diagnosis | Lymph node biopsy, immunohistochemistry |
| Differential diagnosis | Classical Hodgkin lymphoma, Non-Hodgkin lymphoma |
| Prevention | |
| Treatment | Chemotherapy, radiation therapy, monoclonal antibody therapy |
| Medication | |
| Prognosis | Generally good with treatment |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | |
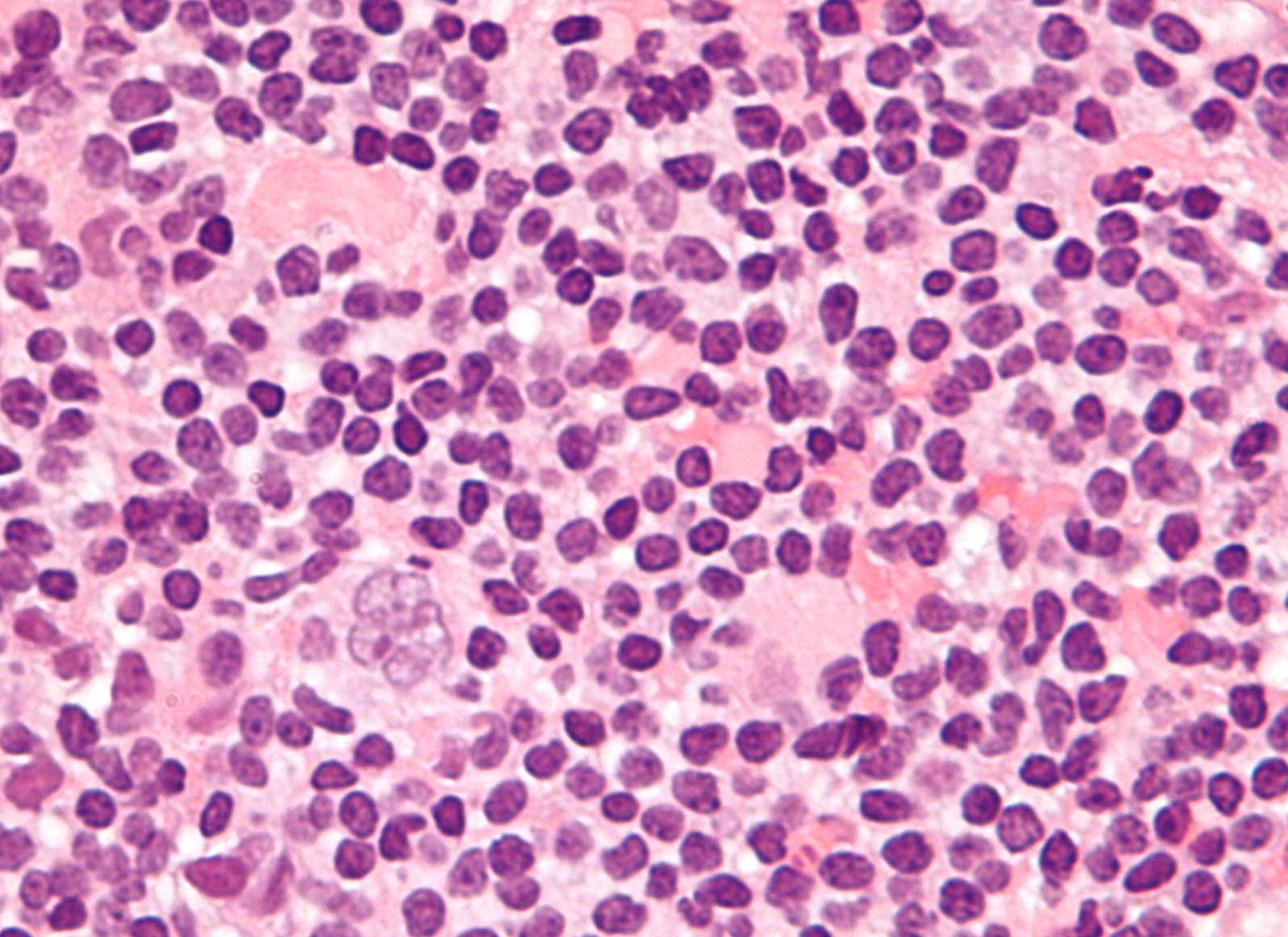
Nodular Lymphocyte Predominant Hodgkin Lymphoma (NLPHL) is a rare subtype of Hodgkin lymphoma, which itself is a type of lymphoma, a cancer originating from lymphocytes. Lymphocytes are a kind of white blood cells that are part of the immune system. NLPHL is characterized by the presence of distinctive cells known as Lymphocyte Predominant (LP) cells or "popcorn cells," which are large cells with a multilobed nucleus resembling popcorn. This condition is different from the more common Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma (CHL) in its epidemiology, pathology, clinical presentation, and treatment outcomes.
Epidemiology[edit | edit source]
NLPHL accounts for approximately 5% of all Hodgkin lymphoma cases. It has a different age distribution compared to CHL, with peaks in adolescence and late adulthood. The disease is more common in males than in females.
Pathophysiology[edit | edit source]
The hallmark of NLPHL is the presence of LP cells, which are considered to be malignant B cells. These cells are surrounded by a reactive infiltrate of benign lymphocytes, histiocytes, and occasionally eosinophils. Unlike CHL, which often involves the expression of CD30 and CD15 markers on the malignant cells, LP cells in NLPHL typically express B-cell markers such as CD20 and CD45.
Clinical Presentation[edit | edit source]
Patients with NLPHL usually present with painless lymphadenopathy, most commonly affecting cervical and axillary lymph nodes. Systemic symptoms such as fever, night sweats, and weight loss (B symptoms) are less common than in CHL. The disease is often diagnosed at an early stage and tends to follow an indolent course, with slow progression.
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
The diagnosis of NLPHL is based on the histological examination of a lymph node biopsy. The presence of LP cells in a nodular pattern is key to the diagnosis. Immunohistochemistry is used to distinguish NLPHL from CHL and other lymphomas, with LP cells showing positivity for B-cell markers and negativity for CD15 and CD30.
Treatment[edit | edit source]
The treatment of NLPHL depends on the stage and symptoms of the disease. For early-stage NLPHL, localized radiotherapy is often the treatment of choice. Advanced stages may require chemotherapy, with or without radiotherapy. The use of rituximab, a monoclonal antibody targeting CD20, has shown promise in the treatment of NLPHL, especially in relapsed or refractory cases.
Prognosis[edit | edit source]
The prognosis for patients with NLPHL is generally favorable, with high rates of long-term survival. However, the disease can recur, and patients require long-term follow-up. There is also an increased risk of developing secondary malignancies, including non-Hodgkin lymphoma and solid tumors.
Summary[edit | edit source]
Nodular Lymphocyte Predominant Hodgkin Lymphoma is a distinct entity within the spectrum of Hodgkin lymphoma, with unique clinical and pathological features. Despite its indolent nature, careful diagnosis and appropriate treatment are essential to manage the disease effectively and to monitor for potential complications.
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's NYC physician weight loss.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available. Call 718 946 5500.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD



