Chronic progressive external ophthalmoplegia
(Redirected from Ophthalmoplegia myalgia tubular aggregates)
| Chronic progressive external ophthalmoplegia | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | CPEO |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Ptosis, ophthalmoplegia, muscle weakness |
| Complications | N/A |
| Onset | Typically in adulthood |
| Duration | Chronic |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Mitochondrial DNA mutations |
| Risks | Family history of mitochondrial disorders |
| Diagnosis | Clinical diagnosis, genetic testing |
| Differential diagnosis | Myasthenia gravis, Kearns-Sayre syndrome |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Supportive care, eyelid surgery |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Variable, generally progressive |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |
A mitochondrial disorder affecting eye muscles
| Chronic progressive external ophthalmoplegia | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Progressive external ophthalmoplegia, CPEO |
| Pronounce | /Àà…ífŒ∏…ôlmo äÀåpliÀêd í…ô/ |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Gradual paralysis of the extraocular muscles, ptosis, limited eye movement, muscle weakness, exercise intolerance |
| Complications | Dysphagia, cardiomyopathy, sensorineural hearing loss, diabetes mellitus |
| Onset | Typically in young adulthood or middle age |
| Duration | Chronic and progressive |
| Types | CPEO, CPEO plus (includes systemic symptoms) |
| Causes | Mutations in mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) or nuclear DNA, such as POLG, TWNK, RRM2B |
| Risks | Family history of mitochondrial disease, genetic mutations |
| Diagnosis | Muscle biopsy, genetic testing, EMG, MRI, ophthalmological exam |
| Differential diagnosis | Myasthenia gravis, Graves' ophthalmopathy, Kearns–Sayre syndrome, oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy |
| Prevention | None known; genetic counseling may be helpful |
| Treatment | Supportive care, eyelid surgery, eye protection, physical therapy, aids for ptosis |
| Medication | No disease-specific drugs; coenzyme Q10 and vitamins may be used supportively |
| Prognosis | Slowly progressive; often compatible with normal life expectancy |
| Frequency | Rare; exact incidence unknown |
| Deaths | Not typically fatal; related systemic complications may affect prognosis |
Chronic progressive external ophthalmoplegia (CPEO) is a rare neuromuscular disorder characterized by slowly progressive paralysis of the extraocular muscles, which are responsible for controlling eye movements. This condition leads to ptosis (drooping of the eyelids) and limited eye movement, often resulting in diplopia (double vision). CPEO is primarily associated with mitochondrial myopathy, a type of mitochondrial disease.
Pathophysiology[edit | edit source]
CPEO is caused by defects in the mitochondria, the energy-producing structures within cells. These defects can result from mutations in nuclear DNA or mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA). The mutations lead to impaired energy production, particularly affecting tissues with high energy demands, such as the muscles controlling eye movement. The accumulation of dysfunctional mitochondria in these muscles results in their progressive weakness and paralysis.
Clinical Features[edit | edit source]
The hallmark of CPEO is the gradual onset of ophthalmoplegia, which typically begins in adulthood. Patients often present with:
- Ptosis: Drooping of one or both eyelids, which may be the initial symptom.
- Ophthalmoplegia: Limited movement of the eyes in all directions, leading to difficulty in tracking objects and diplopia.
- Facial Weakness: Some patients may experience mild weakness of the facial muscles.
- Muscle Weakness: In some cases, CPEO may be associated with generalized muscle weakness, particularly in the limbs.
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
The diagnosis of CPEO is based on clinical examination, family history, and specialized tests. Key diagnostic tools include:
- Ophthalmologic Examination: To assess the extent of eye movement limitation and ptosis.
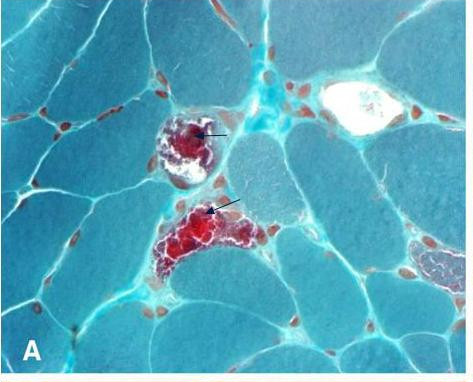
- Muscle Biopsy: May reveal characteristic "ragged-red fibers," indicative of mitochondrial myopathy.
- Genetic Testing: To identify mutations in mtDNA or nuclear DNA associated with CPEO.
- Electromyography (EMG): To evaluate muscle function and detect abnormalities.
Management[edit | edit source]
There is currently no cure for CPEO, and treatment is primarily supportive. Management strategies include:
- Ptosis Surgery: To improve eyelid function and vision.
- Prism Glasses: To alleviate diplopia by correcting eye alignment.
- Physical Therapy: To maintain muscle strength and function.
- Genetic Counseling: For affected individuals and their families to understand the inheritance patterns and risks.
Prognosis[edit | edit source]
CPEO is a progressive condition, but the rate of progression can vary widely among individuals. While the disorder primarily affects eye muscles, some patients may develop additional symptoms related to mitochondrial dysfunction, such as cardiac conduction defects or sensorineural hearing loss.
Related Pages[edit | edit source]
| Mitochondrial diseases | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
see also mitochondrial proteins
|
| Diseases of muscle, neuromuscular junction, and neuromuscular disease | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP1 injections from $125
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program NYC and a clinic to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our W8MD's physician supervised medical weight loss centers in NYC provides expert medical guidance, and offers telemedicine options for convenience.
Why choose W8MD?
- Comprehensive care with FDA-approved weight loss medications including:
- loss injections in NYC both generic and brand names:
- weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion etc.
- Accept most insurances for visits or discounted self pay cost.
- Generic weight loss injections starting from just $125.00 for the starting dose
- In person weight loss NYC and telemedicine medical weight loss options in New York city available
- Budget GLP1 weight loss injections in NYC starting from $125.00 biweekly with insurance!
Book Your Appointment
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss, and Philadelphia medical weight loss Call (718)946-5500 for NY and 215 676 2334 for PA
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's NYC physician weight loss.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available. Call 718 946 5500.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD


