Prader–Willi syndrome
(Redirected from Prader-Willi syndrome)
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Prader–Willi syndrome | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | |
| Specialty | Endocrinology, Genetics |
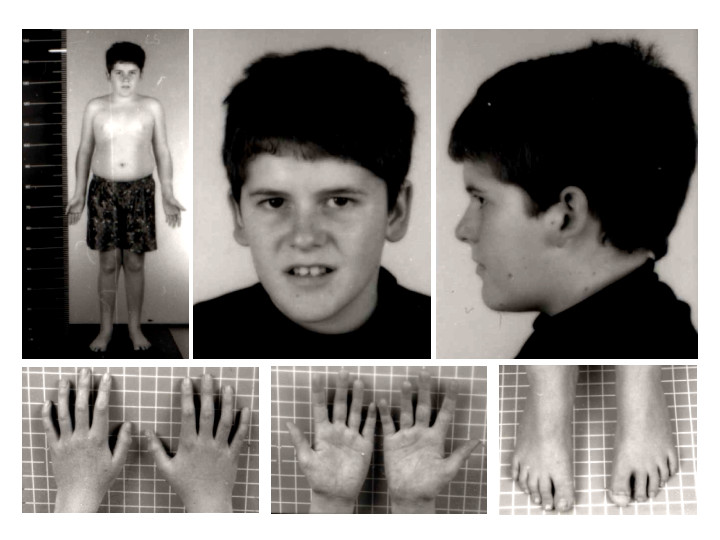
| Symptoms | Hypotonia, feeding difficulties, poor growth, delayed development, hyperphagia, obesity, intellectual disability, behavioral problems |
| Complications | N/A |
| Onset | Infancy |
| Duration | Lifelong |
| Types | |
| Causes | Genetic disorder (loss of function of specific genes on chromosome 15) |
| Risks | |
| Diagnosis | Genetic testing |
| Differential diagnosis | Angelman syndrome, Bardet–Biedl syndrome, Cohen syndrome |
| Prevention | |
| Treatment | Dietary management, hormone therapy, behavioral therapy |
| Medication | Growth hormone |
| Prognosis | |
| Frequency | 1 in 10,000 to 30,000 |
| Deaths | |
Prader-Willi Syndrome (PWS) is a complex genetic disorder characterized by a series of physical, cognitive, and behavioral symptoms. PWS is caused by the loss of function of specific genes on chromosome 15. It is a rare condition, with an estimated incidence of 1 in 15,000 to 1 in 25,000 births.[1]
Genetics[edit | edit source]
PWS is caused by the absence of certain active genes in the region of chromosome 15 that is inherited from the father. This can occur through three main mechanisms: paternal deletion, maternal uniparental disomy, or an imprinting defect.[2]
Symptoms[edit | edit source]
The symptoms of Prader-Willi Syndrome can be grouped into two stages: those seen in infancy and those that develop during childhood.
Infantile Stage[edit | edit source]
In newborns, PWS is characterized by:
- Poor muscle tone (hypotonia), leading to a weak cry and a poor sucking reflex
- Poor feeding and failure to thrive
- Distinct facial features, such as almond-shaped eyes and a narrow forehead
- Undescended testicles in boys
- Slow physical and mental development[3]
Childhood Stage[edit | edit source]
As children with PWS grow older, the syndrome is marked by:
- Excessive hunger and food-seeking behavior, often leading to rapid weight gain and obesity
- Development of type 2 diabetes
- Short stature and small hands and feet
- Intellectual impairment, typically in the mild to moderate range
- Behavioral problems, including temper tantrums and stubbornness
- Light skin and hair compared to family members
- Hypogonadism leading to incomplete sexual development and infertility[4]
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
Diagnosis of PWS involves a combination of clinical findings and genetic testing. Methylation analysis is the standard initial diagnostic test, which can detect over 99% of cases. Further genetic testing can then be performed to determine the specific genetic cause.[5]
Management[edit | edit source]
While there is currently no cure for Prader-Willi Syndrome, there are treatments available to manage its various symptoms. These may include a strict diet and regular physical activity to manage weight, hormone therapy (such as growth hormone or sex hormones), behavioral therapies, and educational support.[6]
Growth Hormone Therapy[edit | edit source]
Growth hormone therapy can help children with PWS reach a more normal height and can also improve their muscle tone, physical strength, and agility.[7]
Dietary Management[edit | edit source]
Dietary management is essential in individuals with PWS due to the risk of obesity from overeating. A low-calorie, well-balanced diet is typically recommended, along with close monitoring of the individual's weight.[8]
Behavioral Therapy[edit | edit source]
Behavioral therapies can help manage the behavioral problems associated with PWS. This may include cognitive-behavioral therapy, psychotherapy, and social skills training.[9]
Educational Support[edit | edit source]
Individuals with PWS often benefit from special education services due to their intellectual impairment. An individualized education plan (IEP) can be developed to meet the specific needs of the child.[10]
Prognosis[edit | edit source]
With appropriate management, individuals with PWS can lead fulfilling lives. However, they often require lifelong care and support due to the chronic nature of the condition. The main cause of mortality in PWS is complications related to obesity, such as heart disease and type 2 diabetes, but this risk can be reduced with proper management.[11]
Research Directions[edit | edit source]
Future research in PWS is focused on understanding the specific functions of the genes involved in the syndrome, exploring potential curative treatments, and developing better strategies for managing the symptoms of the condition.[12]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Prader-Willi Syndrome - GeneReviews¬Æ(link). NCBI Bookshelf. Accessed 2023-05-03.
- ↑ Prader-Willi syndrome(link). Genetics Home Reference. Accessed 2023-05-03.
- ↑ Prader-Willi syndrome - Symptoms and causes(link). Mayo Clinic. Accessed 2023-05-03.
- ↑ Prader-Willi syndrome - Symptoms(link). NHS. Accessed 2023-05-03.
- ↑ Diagnosis & Testing(link). Prader-Willi Syndrome Association (USA). Accessed 2023-05-03.
- ↑ Treatment & Management(link). Prader-Willi Syndrome Association (USA). Accessed 2023-05-03.
- ↑ The benefits and drawbacks of growth hormone treatment in Prader-Willi syndrome(link). NCBI. Accessed 2023-05-03.
- ↑ Dietary Management(link). Prader-Willi Syndrome Association (USA). Accessed 2023-05-03.
- ↑ Behavioral Aspects of Prader-Willi Syndrome(link). NCBI. Accessed 2023-05-03.
- ↑ Education(link). Prader-Willi Syndrome Association (USA). Accessed 2023-05-03.
- ↑ Prader-Willi syndrome: an update and review for the primary pediatrician(link). NCBI. Accessed 2023-05-03.
- ↑ Prader-Willi Research(link). Foundation for Prader-Willi Research. Accessed 2023-05-03.
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP1 injections from $125
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program NYC and a clinic to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our W8MD's physician supervised medical weight loss centers in NYC provides expert medical guidance, and offers telemedicine options for convenience.
Why choose W8MD?
- Comprehensive care with FDA-approved weight loss medications including:
- loss injections in NYC both generic and brand names:
- weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion etc.
- Accept most insurances for visits or discounted self pay cost.
- Generic weight loss injections starting from just $125.00 for the starting dose
- In person weight loss NYC and telemedicine medical weight loss options in New York city available
- Budget GLP1 weight loss injections in NYC starting from $125.00 biweekly with insurance!
Book Your Appointment
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss, and Philadelphia medical weight loss Call (718)946-5500 for NY and 215 676 2334 for PA
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's NYC physician weight loss.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available. Call 718 946 5500.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD





