Spinal cord injury
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Spinal cord injury | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Loss of sensation, paralysis, incontinence |
| Complications | Pressure ulcers, deep vein thrombosis, autonomic dysreflexia |
| Onset | Sudden |
| Duration | Long-term |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Trauma, tumors, infections, ischemia |
| Risks | Motor vehicle accidents, falls, sports injuries, violence |
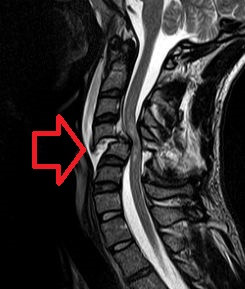
| Diagnosis | Physical examination, imaging studies (X-ray, CT scan, MRI) |
| Differential diagnosis | N/A |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Surgery, medication, physical therapy, occupational therapy |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Varies depending on the level and severity of injury |
| Frequency | Approximately 17,000 new cases per year in the United States |
| Deaths | N/A |
Spinal cord injury (SCI) is a damage to the spinal cord that results in loss of function, such as mobility or feeling. Frequent causes of damage are trauma (car accident, gunshot, falls, etc.) or disease (polio, spina bifida, Friedreich's Ataxia, etc.). The spinal cord does not have to be severed in order for a loss of functioning to occur. In fact, in most people with SCI, the spinal cord is intact, but the damage to it results in loss of functioning. SCI is very different from back injuries such as ruptured disks, spinal stenosis or pinched nerves.
Causes[edit | edit source]
A spinal cord injury can occur either from an injury or from disease. The most common types of SCI include:
- Contusion (bruising of the spinal cord)
- Compression (caused by pressure on the spinal cord)
- Other types of injuries include lacerations (severing or tearing of some nerve fibers, such as damage caused by a gunshot wound), and central cord syndrome (specific damage to the corticospinal tracts of the cervical region of the spinal cord).
Symptoms[edit | edit source]
Symptoms of a spinal cord injury may include:
- Loss of movement
- Loss of sensation, including the ability to feel heat, cold and touch
- Loss of bowel or bladder control
- Exaggerated reflex activities or spasms
- Changes in sexual function, sexual sensitivity and fertility
- Pain or an intense stinging sensation caused by damage to the nerve fibers in your spinal cord
- Difficulty breathing, coughing or clearing secretions from your lungs
Treatment[edit | edit source]
Treatment for a spinal cord injury often begins with surgery to relieve pressure on the spinal cord and manage any fractures. Thereafter, medications and therapies are used to manage symptoms and improve quality of life. These may include:
- Medications to manage pain and other symptoms
- Immobilization to allow the spine to heal
- Surgery to stabilize the spine or prevent further damage
- Rehabilitation therapy to improve mobility and function
Images[edit | edit source]
See also[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's NYC physician weight loss.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available. Call 718 946 5500.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD