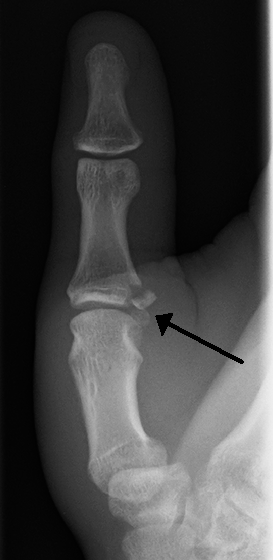
Ulnar collateral ligament injury of the thumb
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Ulnar collateral ligament injury of the thumb | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Skier's thumb, Gamekeeper's thumb |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | Orthopedic surgery |
| Symptoms | Pain, swelling, instability of the thumb |
| Complications | Chronic pain, arthritis |
| Onset | Acute or chronic |
| Duration | Varies |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Trauma, repetitive stress |
| Risks | Skiing, hunting, sports |
| Diagnosis | Physical examination, X-ray, MRI |
| Differential diagnosis | Thumb fracture, arthritis |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Splinting, surgery |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Generally good with treatment |
| Frequency | Common in athletes |
| Deaths | N/A |
An ulnar collateral ligament injury of the thumb, also known as "gamekeeper's thumb" or "skier's thumb," is a common injury to the thumb that involves the tearing or stretching of the ulnar collateral ligament (UCL) at the metacarpophalangeal joint. This ligament is crucial for the stability of the thumb, particularly in pinching and gripping activities.
History[edit | edit source]
The term "gamekeeper's thumb" was first coined in 1955 by Campbell, who observed this injury in Scottish gamekeepers. The injury was caused by the repetitive stress of breaking the necks of small animals, which led to chronic injury of the UCL. In modern times, the injury is more commonly associated with acute trauma, such as falling on an outstretched hand while holding a ski pole, hence the term "skier's thumb."
Anatomy[edit | edit source]
The ulnar collateral ligament is located on the ulnar side of the thumb's metacarpophalangeal joint. It provides stability to the joint by preventing excessive lateral movement. The ligament can be injured by a forceful abduction of the thumb, which can occur during falls or direct impacts.
Symptoms[edit | edit source]
Symptoms of an ulnar collateral ligament injury include:
- Pain and tenderness on the ulnar side of the thumb
- Swelling and bruising around the joint
- Weakness in pinching or gripping
- Instability of the thumb joint
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
Diagnosis is typically made through a combination of physical examination and imaging studies. The "valgus stress test" is commonly used to assess the stability of the UCL. X-rays may be taken to rule out fractures, and MRI can be used to evaluate the extent of ligament damage.
Treatment[edit | edit source]
Treatment depends on the severity of the injury:
- Non-surgical treatment: Mild injuries may be treated with immobilization using a thumb splint or cast for 4-6 weeks, followed by physical therapy.
- Surgical treatment: Complete tears or injuries with significant instability often require surgical repair to restore thumb function. Surgery involves reattaching the ligament to the bone or reconstructing it using a tendon graft.
Prognosis[edit | edit source]
With appropriate treatment, most individuals recover full function of the thumb. However, delayed treatment or improper healing can lead to chronic instability and arthritis.
See also[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's NYC physician weight loss.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available. Call 718 946 5500.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD