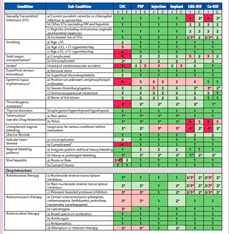
Medical eligibility criteria for contraceptive use
Guidelines for safe contraceptive use based on medical conditions
Medical Eligibility Criteria for Contraceptive Use[edit | edit source]
The Medical Eligibility Criteria for Contraceptive Use (MEC) are guidelines developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) to assist healthcare providers in determining the safety of various contraceptive methods for individuals with specific health conditions or characteristics. These criteria are designed to ensure that individuals can use contraceptive methods safely and effectively, minimizing health risks while maximizing the benefits of contraception.
Overview[edit | edit source]
The MEC guidelines categorize contraceptive methods into four categories based on their safety for individuals with particular medical conditions:
- Category 1: A condition for which there is no restriction for the use of the contraceptive method.
- Category 2: A condition where the advantages of using the method generally outweigh the theoretical or proven risks.
- Category 3: A condition where the theoretical or proven risks usually outweigh the advantages of using the method.
- Category 4: A condition which represents an unacceptable health risk if the contraceptive method is used.
These categories help healthcare providers make informed decisions about prescribing contraceptives, taking into account the individual's health status and personal circumstances.
Application of the Criteria[edit | edit source]
The MEC guidelines are used globally by healthcare providers to guide the prescription of contraceptives. They cover a wide range of contraceptive methods, including oral contraceptives, intrauterine devices (IUDs), injectable contraceptives, implants, barrier methods, and fertility awareness methods.
The criteria take into account various health conditions such as hypertension, diabetes, breast cancer, and thromboembolic disorders. For example, women with a history of venous thromboembolism may be advised against using combined hormonal contraceptives, which fall under Category 3 or 4 depending on the severity of the condition.
Importance of the MEC[edit | edit source]
The MEC guidelines are crucial for ensuring that contraceptive methods are used safely and effectively. They help prevent adverse health outcomes by providing clear recommendations based on the latest scientific evidence. This is particularly important in settings where healthcare resources are limited, and access to specialized medical advice may be restricted.
Updates and Revisions[edit | edit source]
The WHO periodically reviews and updates the MEC guidelines to reflect new research findings and advancements in contraceptive technology. These updates ensure that the guidelines remain relevant and evidence-based, providing healthcare providers with the most current information to support their clinical decisions.
Related Pages[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD