Myopia
(Redirected from Nearsighted)
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Myopia | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Nearsightedness, short-sightedness |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Blurry vision when looking at distant objects, headache, eye strain |
| Complications | Retinal detachment, glaucoma, cataracts |
| Onset | Typically in childhood |
| Duration | Long term |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Genetics, environmental factors |
| Risks | Family history, prolonged near work, lack of outdoor activity |
| Diagnosis | Eye examination |
| Differential diagnosis | Hyperopia, astigmatism |
| Prevention | Outdoor activity, regular eye exams |
| Treatment | Glasses, contact lenses, refractive surgery |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | N/A |
| Frequency | Affects approximately 1.5 billion people globally |
| Deaths | N/A |
Myopia (Near-sightedness)
| Also known as | Near-sightedness, Short-sightedness |
|---|---|
| Condition | Refractive error of the eye |
| Cause | Shape of lens, length of eye |
| Treatment | Glasses, Contact lenses, Surgery |
Introduction[edit | edit source]
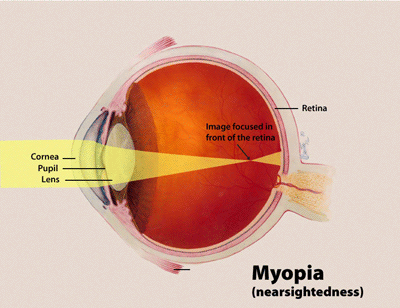
Myopia, popularly referred to as near-sightedness or short-sightedness, is a prevalent refractive error in the eye. This condition interferes with the eye's focusing ability, particularly on distant objects.
Causes[edit | edit source]
Myopia occurs due to either:
- A too curved lens inside the eye.
- An elongated eye structure.
Because of these variations, light entering the eye doesn't focus directly on the retina. Instead, it focuses in front of the retina, leading to a blurred vision for distant objects.
Symptoms and Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
Individuals suffering from myopia often exhibit:
- Blurry vision when looking at distant objects.
- The tendency to squint when viewing television or during attempts to discern far-off objects.
- In some instances, sudden onset of myopia can signal the initial symptom of Type II Diabetes.
Treatment[edit | edit source]
There are multiple methods to rectify myopia:
- Optical aids: Includes wearing glasses with lenses designed to correct the refractive error.
- Contact lenses: Thin lenses placed directly on the eye's surface to provide clear vision.
- Surgery: Procedures like LASIK can reshape the cornea to correct myopia.
Summary[edit | edit source]
With the right intervention, be it optical aids or surgical procedures, myopia can be effectively managed. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent potential complications and enhance the quality of vision.
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP1 injections from $125
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program NYC and a clinic to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our W8MD's physician supervised medical weight loss centers in NYC provides expert medical guidance, and offers telemedicine options for convenience.
Why choose W8MD?
- Comprehensive care with FDA-approved weight loss medications including:
- loss injections in NYC both generic and brand names:
- weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion etc.
- Accept most insurances for visits or discounted self pay cost.
- Generic weight loss injections starting from just $125.00 for the starting dose
- In person weight loss NYC and telemedicine medical weight loss options in New York city available
- Budget GLP1 weight loss injections in NYC starting from $125.00 biweekly with insurance!
Book Your Appointment
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss, and Philadelphia medical weight loss Call (718)946-5500 for NY and 215 676 2334 for PA
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's NYC physician weight loss.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available. Call 718 946 5500.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD





