Plummer–Vinson syndrome
(Redirected from Paterson-Kelly syndrome)
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Plummer–Vinson syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Paterson–Brown–Kelly syndrome, Sideropenic dysphagia |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | Gastroenterology, Hematology |
| Symptoms | Dysphagia, iron-deficiency anemia, glossitis, cheilosis |
| Complications | Esophageal cancer |
| Onset | |
| Duration | |
| Types | |
| Causes | Iron deficiency |
| Risks | |
| Diagnosis | Blood test, endoscopy |
| Differential diagnosis | Esophageal web, esophageal stricture |
| Prevention | |
| Treatment | Iron supplementation, dietary modification |
| Medication | |
| Prognosis | |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | |
Plummer–Vinson syndrome (PVS), also known as Paterson-Brown-Kelly syndrome or sideropenic dysphagia, is a rare condition characterized by a triad of dysphagia, iron deficiency anemia, and esophageal webs. This syndrome predominantly affects middle-aged women and is associated with an increased risk of developing esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Signs and Symptoms[edit | edit source]
The primary symptoms of Plummer–Vinson syndrome include:
- Dysphagia (difficulty swallowing), often due to the presence of esophageal webs.
- Iron deficiency anemia, which can lead to symptoms such as fatigue, pallor, and weakness.
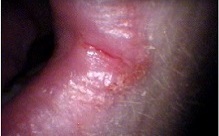
- Glossitis (inflammation of the tongue) and cheilosis (cracks at the corners of the mouth).
Other symptoms may include:
- Koilonychia (spoon-shaped nails)
- Splenomegaly (enlarged spleen)
- Atrophic gastritis
Pathophysiology[edit | edit source]
The exact cause of Plummer–Vinson syndrome is not well understood. However, it is believed that iron deficiency plays a crucial role in the development of esophageal webs and other mucosal changes. Iron is essential for the maintenance of epithelial integrity, and its deficiency may lead to mucosal atrophy and the formation of webs.
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
Diagnosis of Plummer–Vinson syndrome is based on clinical presentation and confirmed through various diagnostic tests, including:
- Barium swallow radiography, which can reveal the presence of esophageal webs.
- Endoscopy, which allows direct visualization and potential biopsy of the esophageal webs.
- Blood tests to confirm iron deficiency anemia, including complete blood count (CBC) and serum iron studies.
Treatment[edit | edit source]
The primary treatment for Plummer–Vinson syndrome involves iron supplementation to correct the iron deficiency anemia. This can lead to the resolution of dysphagia and other symptoms. In some cases, mechanical dilation of the esophagus may be necessary to treat persistent esophageal webs.
Prognosis[edit | edit source]
With appropriate treatment, the prognosis for individuals with Plummer–Vinson syndrome is generally good. However, there is an increased risk of developing esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, necessitating regular monitoring and follow-up.
See also[edit | edit source]
- Dysphagia
- Iron deficiency anemia
- Esophageal webs
- Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- Glossitis
- Cheilosis
- Koilonychia
- Atrophic gastritis
References[edit | edit source]
External Links[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD