Protothecosis
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Protothecosis | |
|---|---|
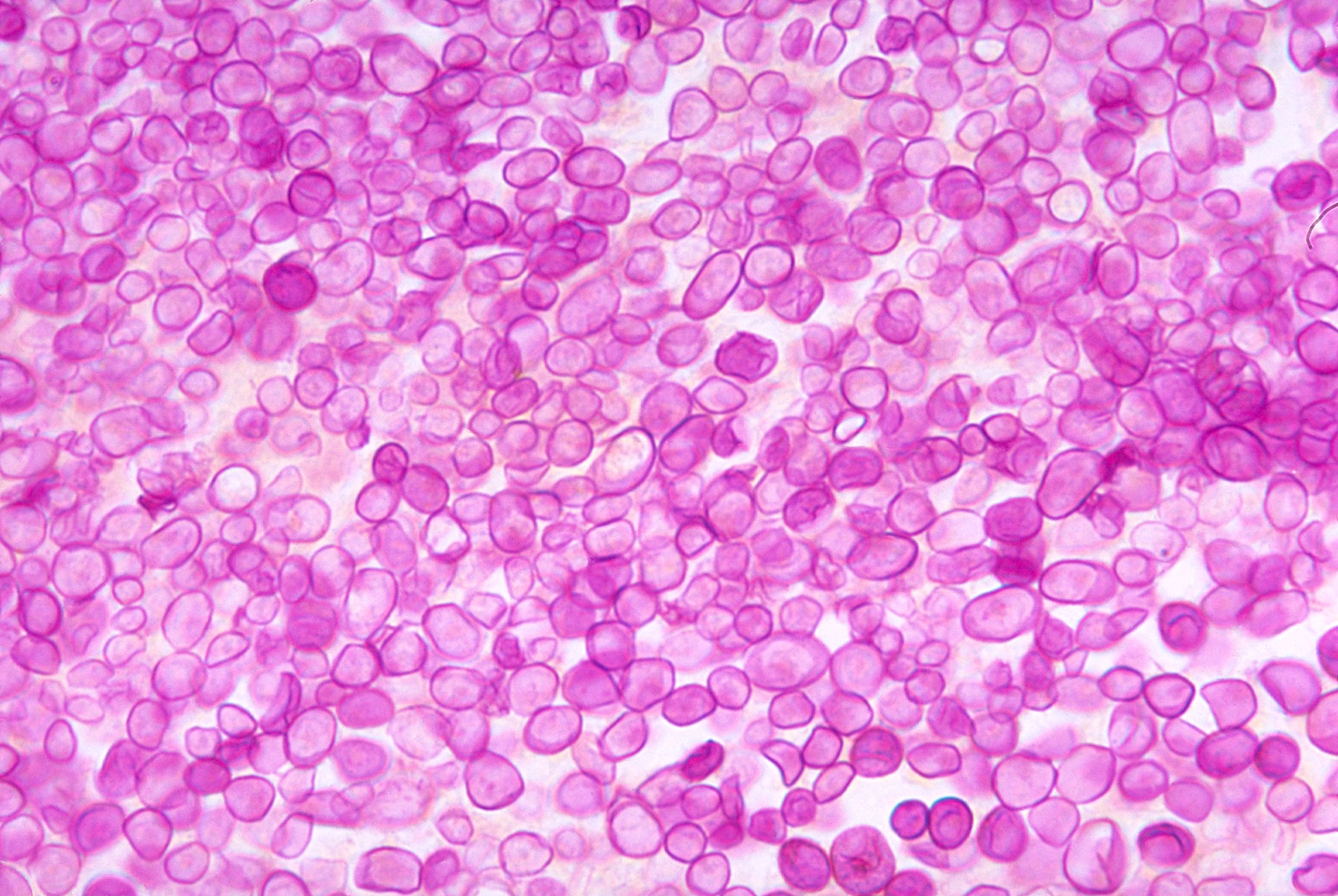
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Cutaneous, subcutaneous, disseminated infections |
| Complications | Meningitis, arthritis, endophthalmitis |
| Onset | Varies |
| Duration | Chronic |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Prototheca species |
| Risks | Immunocompromised individuals |
| Diagnosis | Biopsy, culture, histopathology |
| Differential diagnosis | Fungal infection, bacterial infection |
| Prevention | Avoidance of contaminated water and soil |
| Treatment | Antifungal medications, surgical debridement |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Variable, depends on immune status and treatment |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |
Protothecosis is a rare infection caused by the Prototheca species of algae. It can affect both humans and animals, and is typically seen in immunocompromised individuals. The infection can manifest in a variety of ways, including cutaneous, olecranon bursitis, and disseminated forms.
Etiology[edit | edit source]
Protothecosis is caused by the Prototheca species of algae. These organisms are ubiquitous in the environment and can be found in soil, sewage, and contaminated water. The two species most commonly associated with human disease are Prototheca wickerhamii and Prototheca zopfii.
Clinical Presentation[edit | edit source]
The clinical presentation of protothecosis can vary widely depending on the form of the disease. The cutaneous form typically presents as nodules or ulcers on the skin, while the olecranon bursitis form presents as swelling and pain in the elbow. The disseminated form can affect multiple organ systems and can be life-threatening.
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
Diagnosis of protothecosis is typically made through culture of the organism from clinical specimens. Molecular methods such as PCR can also be used. Histopathology can reveal characteristic morulae within macrophages.
Treatment[edit | edit source]
Treatment of protothecosis typically involves a combination of surgical debridement and antifungal therapy. The antifungal agents amphotericin B and itraconazole have been used with some success.
Epidemiology[edit | edit source]
Protothecosis is a rare disease, with only a few hundred cases reported in the medical literature. It is seen worldwide, but appears to be more common in certain geographic areas such as the southern United States and Japan.
Prevention[edit | edit source]
Prevention of protothecosis involves avoiding contact with contaminated water and soil, particularly for immunocompromised individuals.
See Also[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD




