Germinoma
(Redirected from Seminomatous)
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Germinoma | |
|---|---|
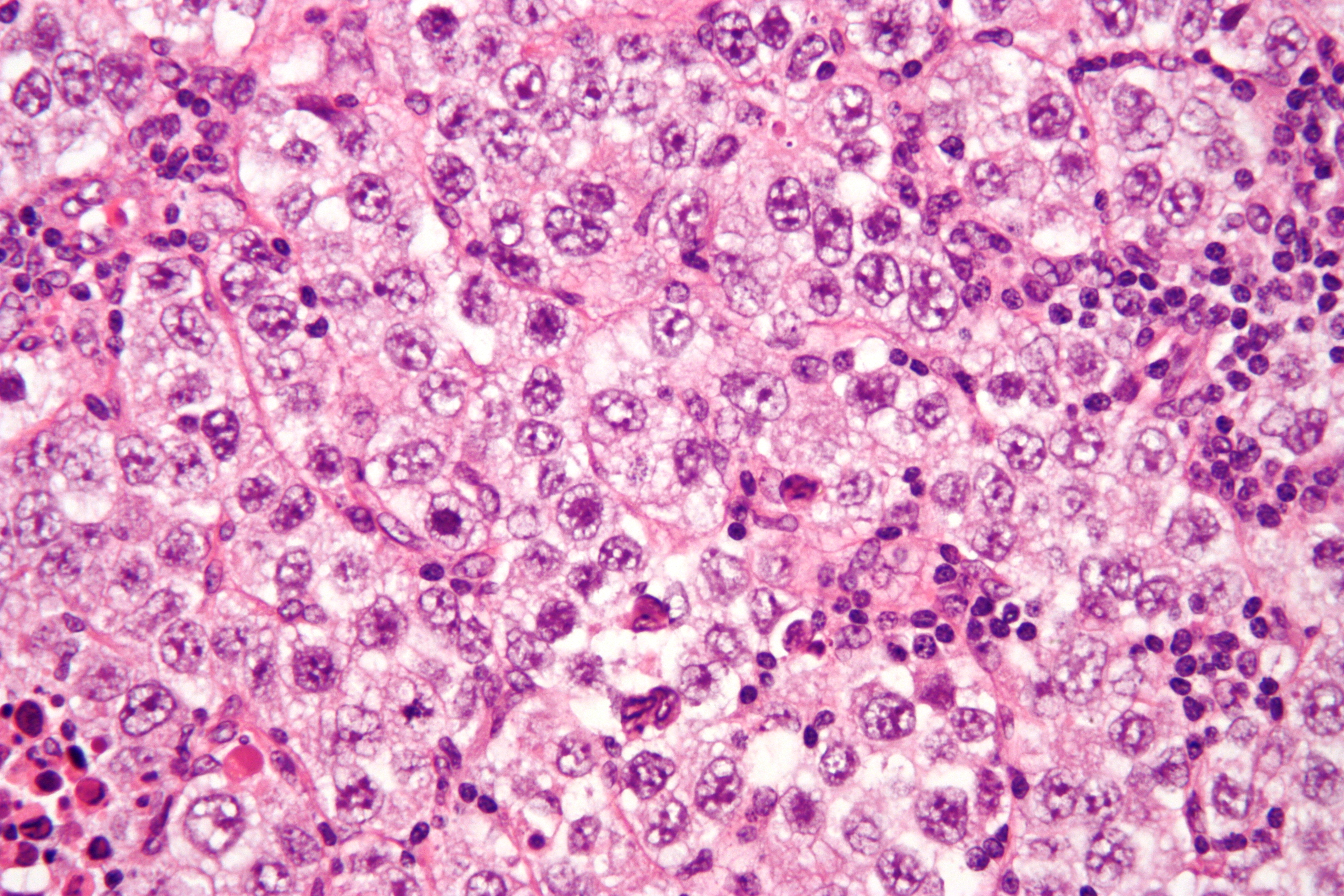
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Headache, nausea, vomiting, vision problems, endocrine dysfunction |
| Complications | Hydrocephalus, diabetes insipidus, hypopituitarism |
| Onset | Typically in adolescence or young adulthood |
| Duration | Variable |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Unknown, possibly genetic and environmental factors |
| Risks | Genetic predisposition, family history |
| Diagnosis | MRI, CT scan, biopsy |
| Differential diagnosis | Teratoma, choriocarcinoma, yolk sac tumor |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Radiation therapy, chemotherapy, surgery |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Generally good with treatment |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |
Germinoma is a type of germ cell tumor that is most commonly found in the brain and gonads (ovaries and testicles). It is a rare, malignant tumor that arises from germ cells, which are the cells responsible for producing sperm and eggs. Germinomas are most often diagnosed in adolescents and young adults, and they have a relatively high survival rate when compared to other types of tumors.
Etiology and Pathogenesis[edit | edit source]
The exact cause of germinomas is not well understood. However, it is believed that genetic and environmental factors may play a role in their development. Germinomas are thought to originate from primordial germ cells that have migrated improperly during the embryonic development phase. These cells can then undergo malignant transformation to become germinomas.
Symptoms[edit | edit source]
The symptoms of a germinoma vary depending on its location. When located in the brain, particularly in the pineal gland or the suprasellar region, symptoms can include headaches, nausea, vomiting, vision problems, and hormonal imbalances. Germinomas in the gonads may present as a palpable mass, pain, or symptoms related to hormonal imbalances.
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
Diagnosis of a germinoma typically involves a combination of imaging studies, such as MRI or CT scan, and biopsy. The biopsy is crucial for confirming the diagnosis, as it allows for histological examination of the tumor cells. Blood tests may also be conducted to look for tumor markers, such as alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG), which can be elevated in some patients with germ cell tumors.
Treatment[edit | edit source]
Treatment for germinomas usually involves a multimodal approach that can include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. The choice of treatment depends on the location and size of the tumor, as well as the patient's overall health. Surgery is often the first step to remove as much of the tumor as possible, followed by radiation therapy and/or chemotherapy to eliminate any remaining cancer cells. Germinomas are generally sensitive to radiation and chemotherapy, which contributes to the high survival rates associated with this type of tumor.
Prognosis[edit | edit source]
The prognosis for patients with germinomas is generally favorable, with high cure rates. The five-year survival rate for patients with germinomas is over 90% when the tumor is properly treated. Early diagnosis and treatment are critical factors that can improve the outcome for patients with this condition.
Epidemiology[edit | edit source]
Germinomas are rare, accounting for a small percentage of all brain tumors. They are most commonly diagnosed in adolescents and young adults, with a slight male predominance when the tumor is located in the brain. When germinomas occur in the gonads, they tend to affect males and females more equally.
See Also[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD


