Acinic cell carcinoma
| Acinic cell carcinoma | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Acinic cell adenocarcinoma |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Swelling in the parotid gland, pain |
| Complications | Facial nerve dysfunction |
| Onset | Typically in adulthood |
| Duration | Long-term |
| Types | Papillary cystic, follicular, solid, microcystic |
| Causes | Unknown |
| Risks | Radiation exposure, genetic predisposition |
| Diagnosis | Biopsy, imaging studies |
| Differential diagnosis | Pleomorphic adenoma, mucoepidermoid carcinoma |
| Prevention | None known |
| Treatment | Surgery, radiation therapy |
| Medication | None specific |
| Prognosis | Generally good with treatment |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |
A type of salivary gland cancer
Acinic cell carcinoma is a rare type of salivary gland cancer that primarily affects the parotid gland, which is the largest of the salivary glands located near the ear. This type of carcinoma is characterized by its slow growth and relatively low potential for metastasis compared to other salivary gland cancers.
Pathophysiology[edit | edit source]
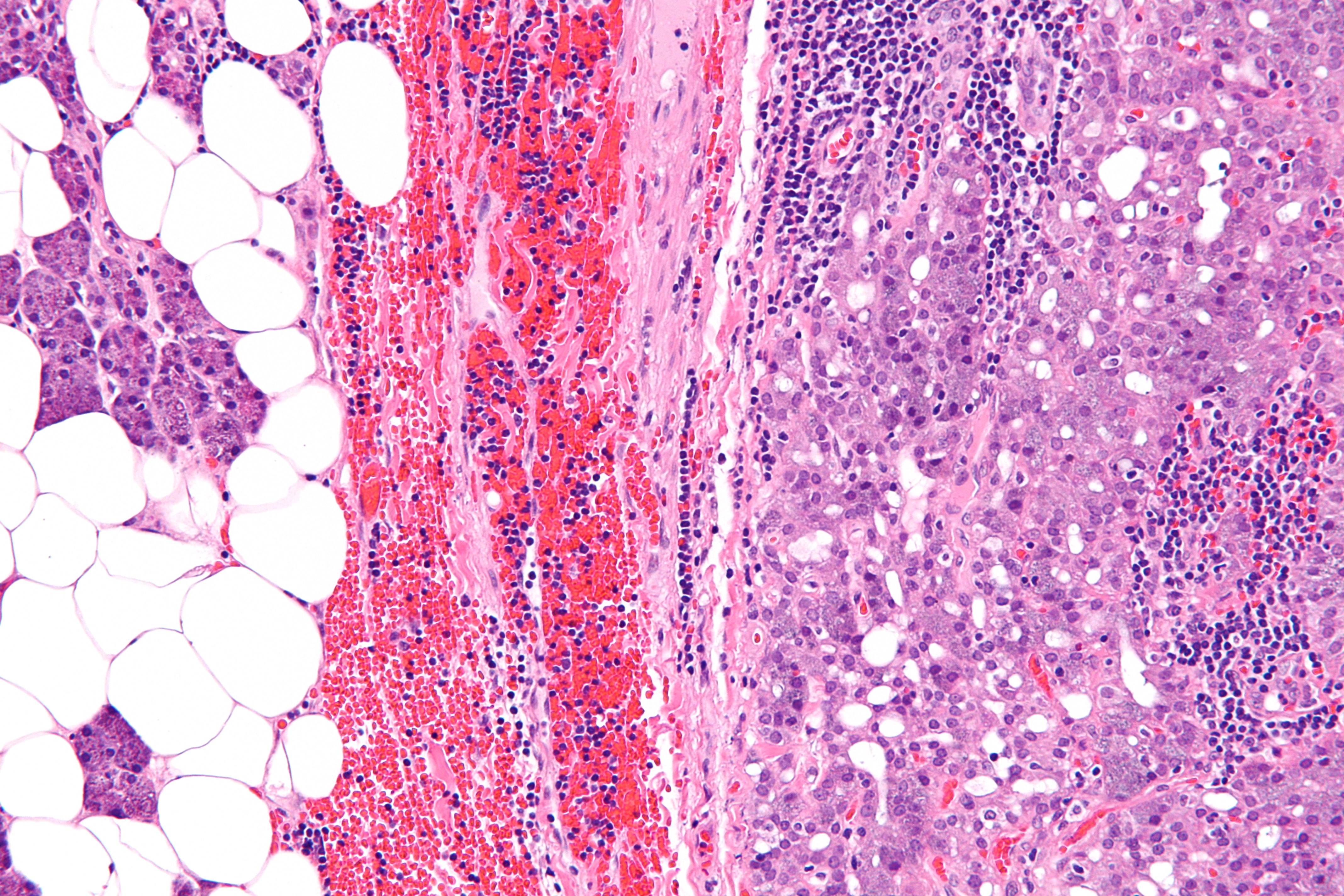
Acinic cell carcinoma arises from the acinar cells of the salivary glands, which are responsible for producing saliva. These tumors are typically composed of cells that resemble normal acinar cells, and they can exhibit a variety of growth patterns, including solid, microcystic, papillary-cystic, and follicular.
The histology of acinic cell carcinoma is notable for its diversity, with tumor cells often showing granular cytoplasm due to the presence of zymogen granules. This feature can help distinguish acinic cell carcinoma from other types of salivary gland tumors.
Clinical Presentation[edit | edit source]
Patients with acinic cell carcinoma often present with a painless, slow-growing mass in the region of the parotid gland. In some cases, the tumor may cause facial nerve dysfunction if it invades nearby structures. Other symptoms can include swelling, discomfort, or a feeling of fullness in the affected area.
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
The diagnosis of acinic cell carcinoma typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging studies, and biopsy. Imaging techniques such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI can help assess the extent of the tumor and its relationship to surrounding structures. A definitive diagnosis is made through histopathological examination of a biopsy specimen.
Treatment[edit | edit source]
The primary treatment for acinic cell carcinoma is surgical resection, often involving a parotidectomy to remove the affected gland. The extent of surgery depends on the size and location of the tumor, as well as its proximity to critical structures such as the facial nerve.
In some cases, radiation therapy may be recommended postoperatively, especially if there are concerns about residual disease or if the tumor exhibits aggressive features. Chemotherapy is generally not a primary treatment modality for acinic cell carcinoma but may be considered in cases of metastatic disease.
Prognosis[edit | edit source]
The prognosis for patients with acinic cell carcinoma is generally favorable, with a high rate of long-term survival. However, the risk of recurrence and metastasis, although lower than in other salivary gland cancers, still exists. Factors influencing prognosis include tumor size, histological grade, and the presence of perineural invasion.
Related Pages[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD
