Anaplastic large-cell lymphoma
(Redirected from Anaplastic large cell lymphoma)
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Anaplastic large-cell lymphoma | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Lymphadenopathy, fever, weight loss, night sweats |
| Complications | Immunodeficiency, infection |
| Onset | Variable |
| Duration | Chronic |
| Types | Primary cutaneous anaplastic large-cell lymphoma, Systemic anaplastic large-cell lymphoma |
| Causes | Unknown, possible genetic mutations |
| Risks | Genetic predisposition, immunosuppression |
| Diagnosis | Biopsy, immunohistochemistry |
| Differential diagnosis | Hodgkin lymphoma, Non-Hodgkin lymphoma, Lymphoblastic lymphoma |
| Prevention | None |
| Treatment | Chemotherapy, radiation therapy, stem cell transplant |
| Medication | Brentuximab vedotin, CHOP chemotherapy |
| Prognosis | Variable, depends on subtype and stage |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |
Anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (ALCL) is a type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma that is characterized by the presence of large, atypical lymphoid cells. It is a rare form of lymphoma that can occur in both children and adults. ALCL is classified as a T-cell lymphoma, meaning it originates from T lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell that plays a crucial role in the immune system.
Classification[edit | edit source]
ALCL is divided into two main types based on the presence or absence of a specific genetic abnormality involving the anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) gene:
- ALK-positive ALCL: This type is more common in children and young adults. It is characterized by the presence of a translocation involving the ALK gene, which leads to the expression of an abnormal ALK protein that promotes cell growth and survival.
- ALK-negative ALCL: This type is more common in older adults and does not have the ALK gene rearrangement. It tends to have a more aggressive clinical course compared to ALK-positive ALCL.
Clinical Presentation[edit | edit source]
Patients with ALCL may present with a variety of symptoms, including:
- Lymphadenopathy: Swelling of the lymph nodes, which may be painless.
- B symptoms: Fever, night sweats, and weight loss.
- Extranodal involvement: ALCL can affect organs outside the lymphatic system, such as the skin, liver, lungs, and bones.
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
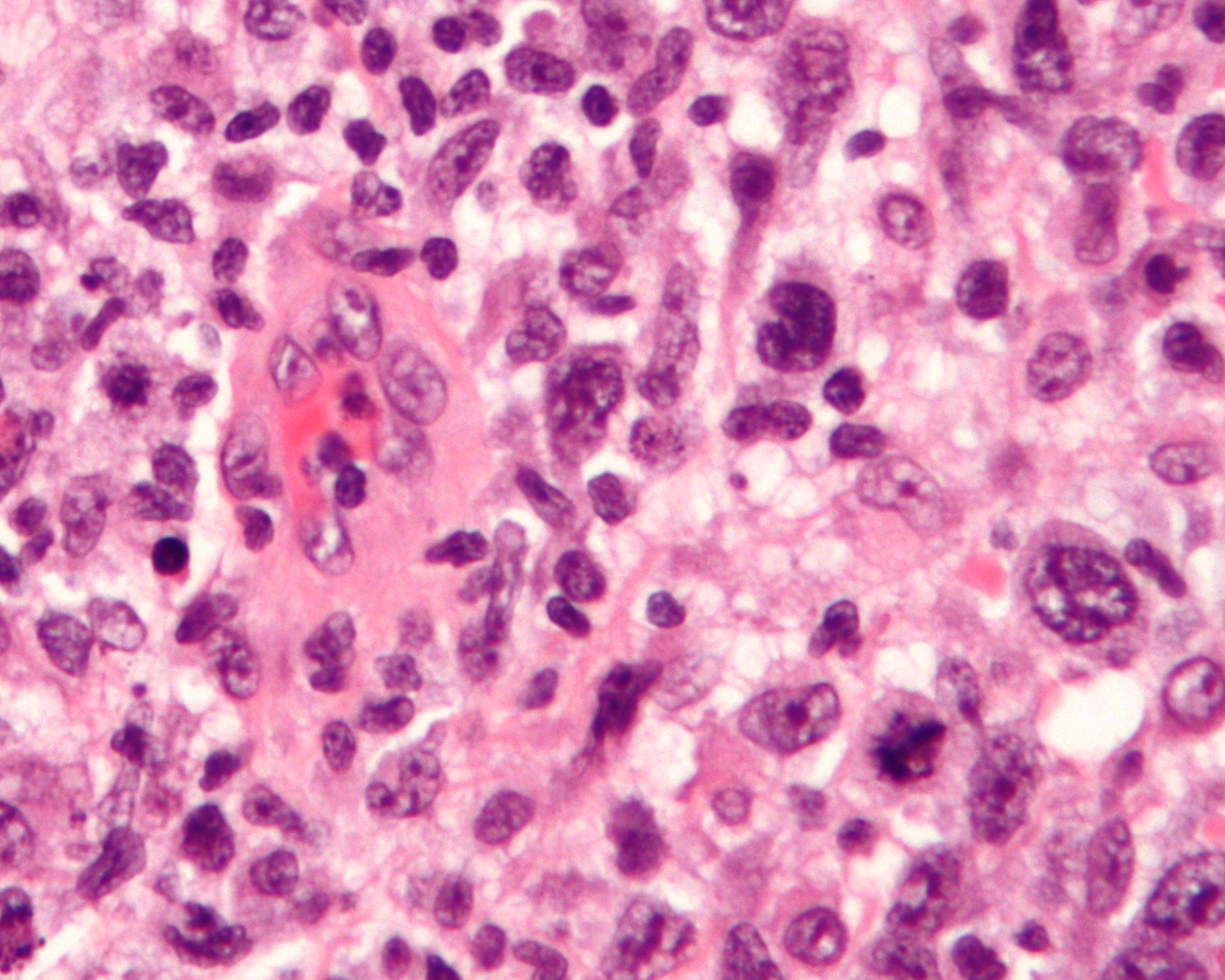
The diagnosis of ALCL is made through a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging studies, and biopsy of affected tissue. Histological examination reveals large, pleomorphic cells with abundant cytoplasm and horseshoe-shaped nuclei. Immunohistochemistry is used to detect the expression of CD30, a marker that is typically positive in ALCL cells.
Treatment[edit | edit source]
The treatment of ALCL depends on the subtype and stage of the disease. Common treatment options include:
- Chemotherapy: Regimens such as CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone) are commonly used.
- Targeted therapy: For ALK-positive ALCL, ALK inhibitors such as crizotinib may be used.
- Radiation therapy: May be used in certain cases, especially for localized disease.
- Stem cell transplantation: Considered in cases of relapsed or refractory ALCL.
Prognosis[edit | edit source]
The prognosis of ALCL varies depending on the subtype and other factors such as age and overall health. ALK-positive ALCL generally has a better prognosis compared to ALK-negative ALCL. Long-term survival rates are higher in children and young adults compared to older patients.
Related Pages[edit | edit source]
| Lymphomas | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
This lymphoma-related article is a stub.
|
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD

