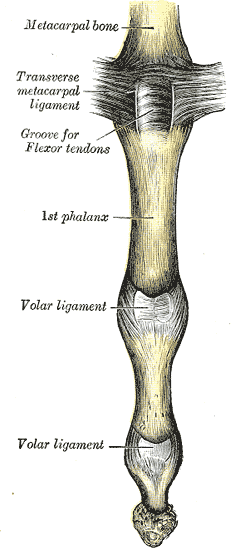
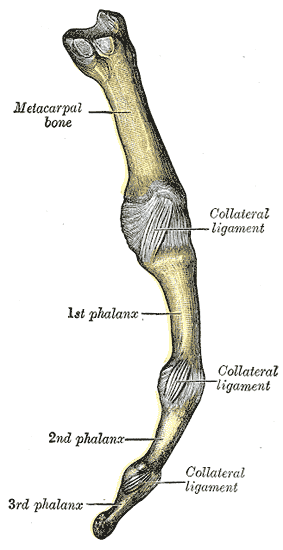
Articulations of the Digits
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
Anatomy > Gray's Anatomy of the Human Body > III. Syndesmology > 6k. Articulations of the Digits
Henry Gray (1821–1865). Anatomy of the Human Body. 1918.
Articulations of the Digits of the Hand[edit | edit source]
(Articulationes Digitorum Manus; Interphalangeal Joints)
The articulations of the fingers—specifically the interphalangeal joints—are a series of hinge joints that permit flexion and extension between the phalanges of the hand.
There are two interphalangeal joints in each finger:
- The proximal interphalangeal joint (PIP) – between the proximal and middle phalanges.
- The distal interphalangeal joint (DIP) – between the middle and distal phalanges.
The thumb, having only two phalanges, possesses a single interphalangeal joint.
Ligaments of the Interphalangeal Joints[edit | edit source]
Each interphalangeal joint is stabilized by three primary ligaments:
- Palmar ligament (volar plate): A thick, fibrocartilaginous band that reinforces the anterior side of the joint capsule and limits hyperextension.
- Collateral ligaments: Paired medial and lateral bands that provide lateral stability and help guide motion during flexion and extension.
- The extensor tendons serve the function of posterior ligaments, as the joints lack distinct posterior reinforcement.
Movements[edit | edit source]
The interphalangeal joints permit the following:
- Flexion: Bending the finger toward the palm.
- Extension: Straightening the finger from a flexed position.
Flexion is more pronounced at the proximal interphalangeal joint (PIP) than at the distal interphalangeal joint (DIP). Extension is restricted by the volar and collateral ligaments.
Muscles Acting on the Joints of the Digits[edit | edit source]
Metacarpophalangeal Joints (MCP)[edit | edit source]
- Flexion:
Flexor digitorum superficialis Flexor digitorum profundus Lumbricals Palmar interossei and dorsal interossei Flexor digiti minimi brevis (for little finger)
- Extension:
Extensor digitorum Extensor indicis Extensor digiti minimi
Interphalangeal Joints[edit | edit source]
- Flexion:
Flexor digitorum superficialis (acts on PIP) Flexor digitorum profundus (acts on PIP and DIP)
- Extension:
Lumbricals and interossei muscles (via their insertion into the extensor expansion) Extensor digitorum plays a limited role directly
Thumb Joints[edit | edit source]
- Flexion of MCP joint:
Flexor pollicis brevis Flexor pollicis longus
- Extension of MCP joint:
- Flexion of interphalangeal joint:
- Extension of interphalangeal joint:
Functional Importance[edit | edit source]
The interphalangeal and metacarpophalangeal joints are essential for precise hand movements, grasping, and manual dexterity. These joints are stabilized by a complex interplay of passive (ligaments) and dynamic (muscular) support systems. Disruption of any of these structures can result in impaired function, such as in cases of arthritis, tendon injury, or joint instability.
See Also[edit | edit source]
- Phalanges
- Hand
- Extensor mechanism of the hand
- Flexor tendons of the hand
- Interphalangeal joints of the foot
| Joints and ligaments of the arm | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Gray's Anatomy[edit source]
- Gray's Anatomy Contents
- Gray's Anatomy Subject Index
- About Classic Gray's Anatomy
- Glossary of anatomy terms
Anatomy atlases (external)[edit source]
[1] - Anatomy Atlases
| Human systems and organs | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Adapted from the Classic Grays Anatomy of the Human Body 1918 edition (public domain)
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Deepika vegiraju, Prab R. Tumpati, MD