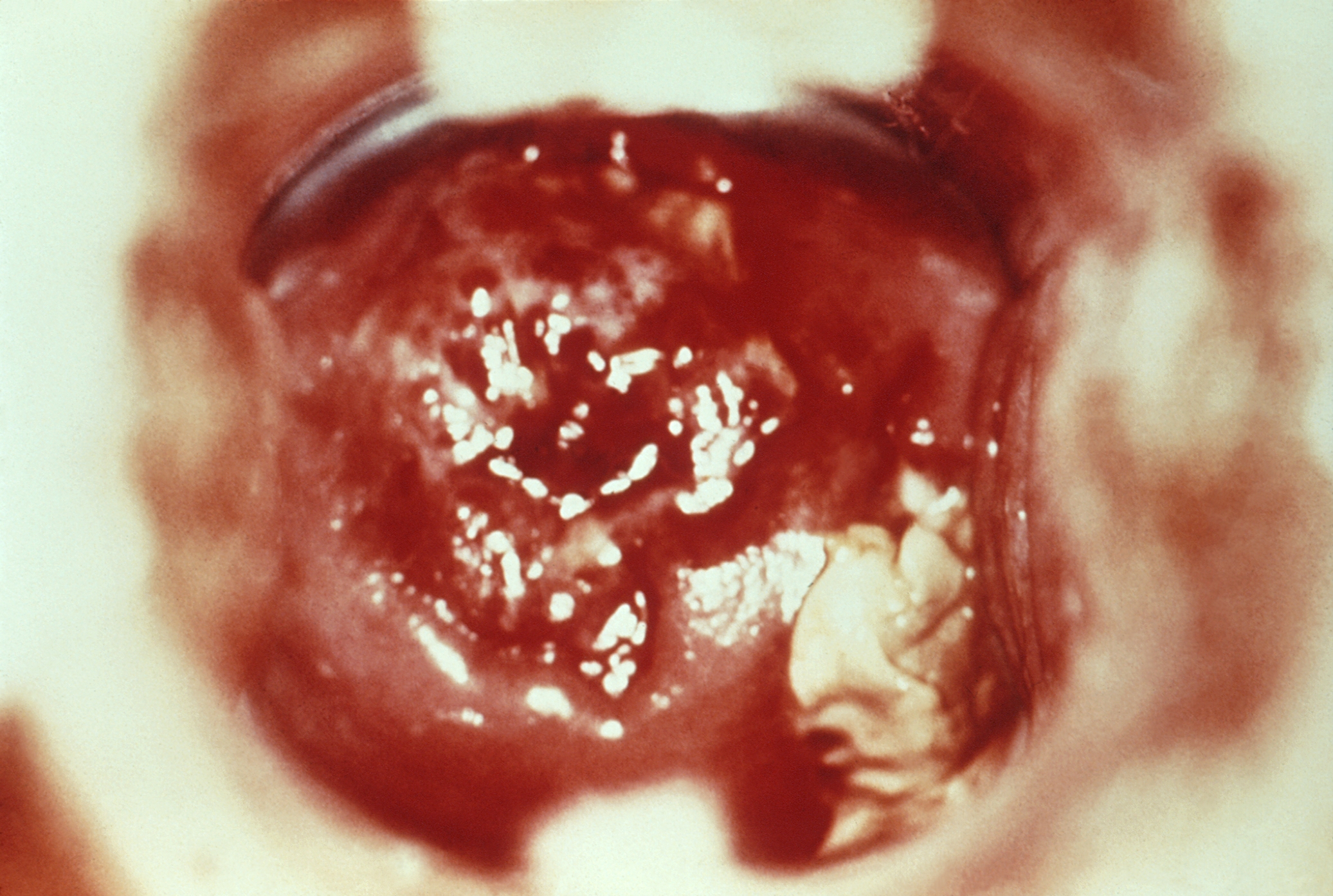
Cervicitis
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Cervicitis | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Vaginal discharge, pain during intercourse, vaginal bleeding |
| Complications | Pelvic inflammatory disease, infertility |
| Onset | |
| Duration | |
| Types | Infectious cervicitis, non-infectious cervicitis |
| Causes | Sexually transmitted infections, allergic reactions, irritants |
| Risks | Multiple sexual partners, unprotected sex |
| Diagnosis | Pelvic examination, Pap smear, culture test |
| Differential diagnosis | Vaginitis, endometritis |
| Prevention | Safe sex, regular screening |
| Treatment | Antibiotics, antiviral drugs, avoidance of irritants |
| Medication | Azithromycin, doxycycline, acyclovir |
| Prognosis | Generally good with treatment |
| Frequency | Common |
| Deaths | N/A |
Cervicitis is an inflammation of the cervix, the lower, narrow end of the uterus that opens into the vagina. Cervicitis can be caused by a number of infections, including those transmitted through sexual contact such as Chlamydia and Gonorrhea, as well as other types of infections that are not sexually transmitted. Symptoms of cervicitis can include vaginal discharge, bleeding between periods or after sexual intercourse, and pelvic pain. However, many women do not experience any symptoms, which can lead to the condition going undiagnosed and untreated.
Causes[edit | edit source]
Cervicitis is most commonly caused by sexually transmitted infections (STIs) like Chlamydia and Gonorrhea. Other causes can include Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV), Human Papillomavirus (HPV), and bacterial overgrowth such as bacterial vaginosis. Non-infectious causes can include allergies to chemical irritants such as spermicides or latex in condoms, and physical irritation from intrauterine devices (IUDs) or tampons.
Symptoms[edit | edit source]
Symptoms of cervicitis may include:
- Abnormal vaginal discharge that may be yellow or green in color and have a foul smell
- Vaginal bleeding between periods or after intercourse
- Pain during intercourse
- Pelvic pain
- A burning sensation during urination
It's important to note that many women with cervicitis do not experience any symptoms. Regular gynecological exams are crucial for early detection and treatment.
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
Diagnosis of cervicitis involves a physical examination, including a pelvic exam, during which a healthcare provider may notice redness, swelling, or discharge from the cervix. Laboratory tests, such as swabs from the cervix, can be used to detect specific infections like Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, or HPV.
Treatment[edit | edit source]
Treatment for cervicitis depends on the underlying cause. If cervicitis is caused by an STI, antibiotics or antiviral medications may be prescribed. It's important for sexual partners to be treated simultaneously to prevent reinfection. For non-infectious causes, avoiding the irritant or changing the behavior that caused the irritation may be recommended.
Prevention[edit | edit source]
Preventive measures for cervicitis include practicing safe sex by using condoms, limiting the number of sexual partners, and undergoing regular STI screenings. Vaccination against HPV can also help prevent cervicitis caused by HPV infections.
Complications[edit | edit source]
If left untreated, cervicitis can lead to serious complications, including pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), which can cause infertility or ectopic pregnancy. It can also increase the risk of contracting HIV if exposed to the virus.
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP1 injections from $125
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program NYC and a clinic to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our W8MD's physician supervised medical weight loss centers in NYC provides expert medical guidance, and offers telemedicine options for convenience.
Why choose W8MD?
- Comprehensive care with FDA-approved weight loss medications including:
- loss injections in NYC both generic and brand names:
- weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion etc.
- Accept most insurances for visits or discounted self pay cost.
- Generic weight loss injections starting from just $125.00 for the starting dose
- In person weight loss NYC and telemedicine medical weight loss options in New York city available
- Budget GLP1 weight loss injections in NYC starting from $125.00 biweekly with insurance!
Book Your Appointment
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss, and Philadelphia medical weight loss Call (718)946-5500 for NY and 215 676 2334 for PA
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's NYC physician weight loss.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available. Call 718 946 5500.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD




