Granulosa cell tumour
(Redirected from Granulosa cell tumor)
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Granulosa cell tumour | |
|---|---|
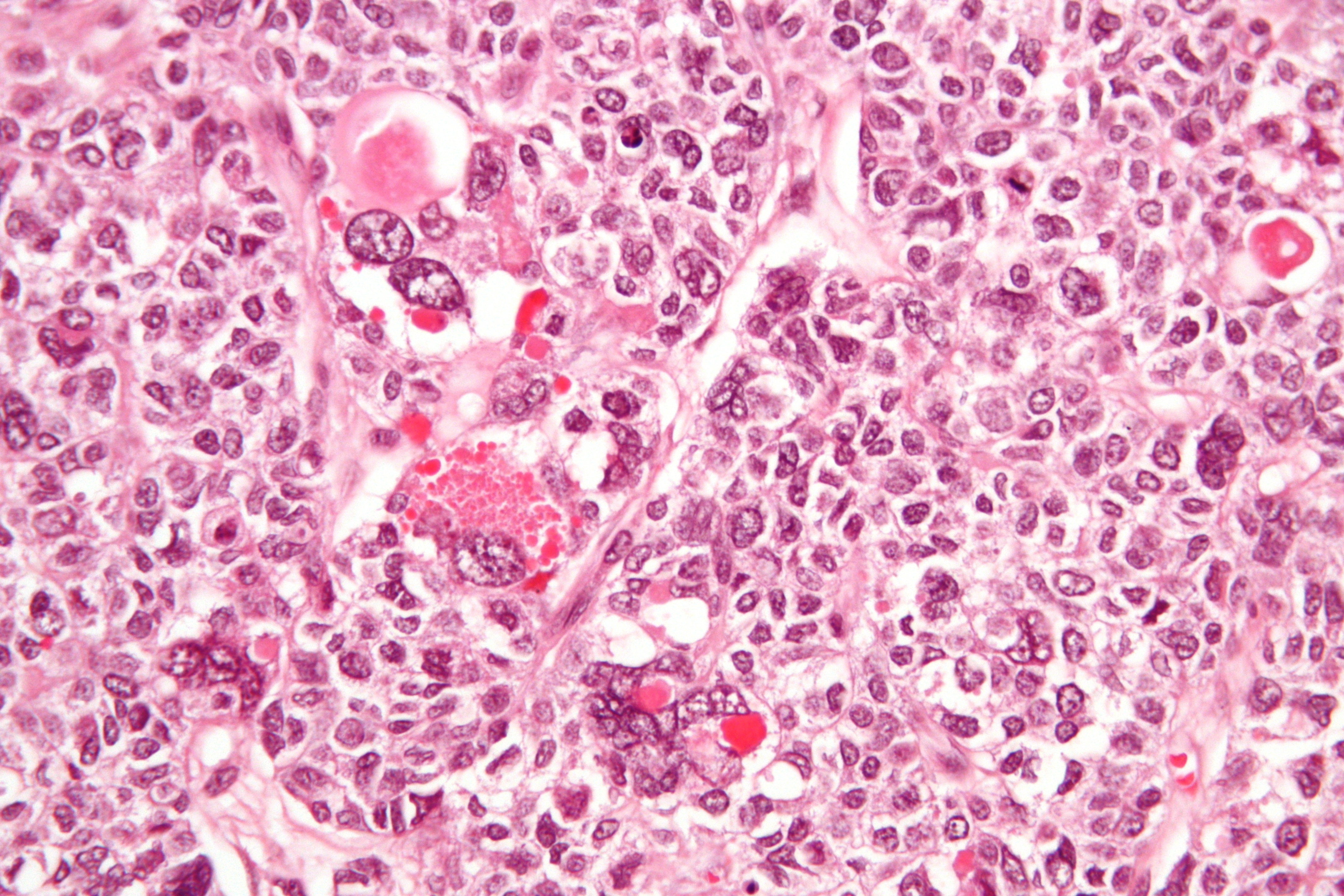
| |
| Synonyms | Granulosa cell tumor |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Abdominal pain, bloating, menstrual irregularities |
| Complications | Infertility, malignancy |
| Onset | Typically adulthood |
| Duration | Variable |
| Types | Adult granulosa cell tumour, Juvenile granulosa cell tumour |
| Causes | Unknown |
| Risks | Genetic mutations, hormonal factors |
| Diagnosis | Histopathology, imaging studies |
| Differential diagnosis | Ovarian cancer, endometriosis |
| Prevention | None known |
| Treatment | Surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy |
| Medication | Hormonal therapy |
| Prognosis | Generally good with treatment |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | Rare |
Granulosa cell tumour is a type of ovarian cancer that originates from the granulosa cells within the ovary. These tumours are part of a larger group of cancers known as sex cord-stromal tumours, which make up approximately 5% of all ovarian cancers.
Etiology[edit | edit source]
The exact cause of granulosa cell tumours is unknown. However, they are associated with mutations in the FOXL2 gene. This gene is involved in the development and function of the ovaries, and mutations can lead to abnormal growth of granulosa cells.
Symptoms[edit | edit source]
Symptoms of granulosa cell tumours can vary widely, depending on the size and location of the tumour. Common symptoms include abdominal pain, bloating, and irregular menstruation. In some cases, these tumours can produce estrogen, leading to symptoms of estrogen excess such as breast tenderness and menstrual irregularities.
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
Diagnosis of granulosa cell tumours typically involves a combination of physical examination, imaging studies, and biopsy. Imaging studies such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI can help to identify the location and size of the tumour. A biopsy, in which a small sample of tissue is removed for examination under a microscope, can confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment[edit | edit source]
Treatment for granulosa cell tumours typically involves surgery to remove the tumour. This may be followed by chemotherapy or radiation therapy to kill any remaining cancer cells. In some cases, hormone therapy may be used to block the effects of estrogen, which can stimulate the growth of these tumours.
Prognosis[edit | edit source]
The prognosis for granulosa cell tumours is generally good, with a 5-year survival rate of approximately 80%. However, these tumours can recur, so long-term follow-up is necessary.
See also[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's NYC physician weight loss.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available. Call 718 946 5500.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD


