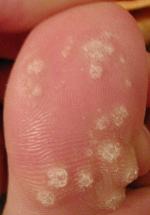
Wart
(Redirected from Verruca vulgaris)
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Wart | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Verruca, verrucae |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Skin growths, usually painless |
| Complications | Pain, bleeding, infection |
| Onset | Childhood, adolescence |
| Duration | Months to years |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Human papillomavirus (HPV) |
| Risks | Immunosuppression, skin trauma |
| Diagnosis | Clinical diagnosis, dermoscopy |
| Differential diagnosis | Callus, corn, molluscum contagiosum |
| Prevention | Avoiding direct contact with warts, maintaining good hygiene |
| Treatment | Salicylic acid, cryotherapy, laser therapy, surgical removal |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Generally good, may resolve spontaneously |
| Frequency | Common |
| Deaths | N/A |
Warts are common, benign skin growths caused by infection with human papillomavirus (HPV). They are characterized by their rough, skin-colored appearance, and can occur anywhere on the body.
Classification[edit | edit source]
Warts come in various types, classified by their appearance and location on the body. Some of the most common types include: Common warts (Verruca vulgaris): These are often found on hands and knees. They have a rough, grainy appearance and a rounded top. Plantar warts (Verruca plantaris): These grow on the soles of the feet and are often painful due to the pressure exerted when standing or walking. Flat warts (Verruca plana): These are smaller and smoother than other types of warts. They tend to grow in large numbers and can occur anywhere, but are most common on the face, neck, hands, and legs. Genital warts (Condyloma acuminatum): These are sexually transmitted and occur on the genital and anal area.
Pathophysiology[edit | edit source]
Warts are caused by various strains of the Human papillomavirus. The virus infects the keratinocytes, causing them to proliferate and leading to the characteristic rough, raised appearance of the wart. The virus is typically contracted through broken skin, which explains why warts often occur on areas of the body that are prone to injury such as the hands and feet.
Treatment[edit | edit source]
Treatment for warts can vary depending on their location and severity, as well as the individual's health status. Options include:
- Topical treatments: Over-the-counter and prescription solutions, gels, and patches containing salicylic acid are often used to treat warts.
- Cryotherapy: This involves freezing the wart with liquid nitrogen, causing it to peel off.
- Minor surgery: If other treatments are ineffective, the wart can be cut out, burned off, or destroyed with a laser.
Prognosis[edit | edit source]
While warts can be bothersome, they are generally harmless and often disappear on their own without treatment. However, they can recur, and individuals with weakened immune systems may have difficulty clearing the virus.
See Also[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD